Introduction
Health Information Systems are revolutionizing the way people access medical services. The information revolution brought about by the development of Information Technology in the last half of the twentieth century is responsible for this phenomenon. The advantages of Health Information Systems in medical services include the use of decision support systems, ease of data capture and retrieval, and the possibility of using analytical techniques to generate information from aggregated medical information (Hersh, 1995). It is important for every physician to have a clear picture of the benefits that a Health Information System can provide. This proposal presents a scientific basis for research into this question. The main research question guiding this process is, “What Roles do Health Information Systems Play in the Work of a Physician?”
Objectives
This research project has three main objectives listed as follows.
- To identify the roles played by physicians in health institutions
Physicians play varied roles in health institutions (Wittrup, 2007). These roles may be medical or administrative in nature. These roles depend on the local laws, workload, and availability of other medical professionals. The roles also depend on the nature of the hospitals the physicians work. It is important to work out the complete range of duties physicians play in different settings. - To identify the bottlenecks that physicians encounter in their work
Physicians must rely on other medical professionals such as nurses, laboratory technicians, and specialized professionals such as radiologists to carry out their work (DiMatteo, 1998). This interdependence in healthcare settings results in various bottlenecks that affect the work of physicians. There is a need to find out the problems physicians face and their gravity in order to figure out how Health Information Systems can play a greater role in eliminating these bottlenecks. - To map out the existing and the future roles that Health Information Systems will play in the work of physicians.
To complete the study, it will be important to examine how the health sector currently employs Health Information Systems available to physicians. It will also be important to identify the future role that Health Information Systems can play in the work of physicians.
Significance
The importance of this research project is that it will provide a fair view of the role that Health Information Systems play in the work of a physician. There is a need to manage the expectations every physician has in relation to the capabilities of Health Information Systems (Smelcer, Miller-Jacobs, & Kantrovich, 2009). Similarly, every physician needs to be aware of the opportunities these systems avail to improve their operational efficiency. Health Information Systems are already part of the medical services infrastructure and it is only fair for physicians to be familiar with the potential and possibilities of these systems in order to increase patient satisfaction.
Literature Review
The roles physicians play in any healthcare setting are in a state of flux. The changes associated with their role emanate from changes taking place in their operating environment. The main drivers behind these changes include legal and regulatory requirements, new knowledge relating to patient care, advances in medical technology, and an increase in the number of specializations in the medical care industry (Ulmer, 2010). The fundamental role of a physician is taking care of patients. In a strict sense, this role involves the identification and assessment of relevant medical facts relating to a patient, reaching a diagnosis, followed by prescribing and implementing treatment (Wittrup, 2007). However, these roles require the physician to play several other roles in order to provide healthcare effectively. DiMatteo (1998) identified several roles a physician must play as part of healthcare provision. These roles include communication with the patient, their families, and other medical professionals playing a part in the care of a patient (DiMatteo, 1998). A physician also has ethical responsibilities to ensure that the medical care given meets the set ethical standards (DiMatteo, 1998). As part of a team of medical professionals, a physician also needs to coordinate and cooperate with the other health professionals, as well as to keep an eye on the cost of providing care to the patient (DiMatteo, 1998). Finally, a physician must understand how to interact with technology because an increasing number of healthcare facilities depend on various technologies to optimize medical care (Ulmer, 2010). This list of roles is not exhaustive, but it provides a general mapping of the nature of roles a physician plays in a health facility.
Health Information Systems have been playing an ever-increasing role in healthcare. A physician must understand how Health Information Systems work in order to offer medical services effectively. There are various types of Health Information Systems. They include Electronic Medical Records (EMR), point of care systems, different types of decision support systems, among others (Hersh, 1995). These systems help physicians in various aspects of their work. First, Health Information Systems make it possible for physicians to record all the treatments given to a particular patient. This forms the basis of medical history for that patient. The advantage of medical histories based on Health Information Systems is that they will be available to all the physicians who will treat the same patient in the future for reference (Smelcer, Miller-Jacobs, & Kantrovich, 2009). Secondly, decision support systems help to generate treatment options for specific patients. Decision support systems aggregate data from different patients and use it to generate optimal treatment procedures. For instance, a physician can compare different treatment regimens for the same medical condition based on cost, effectiveness, and suitability to a case without the need for proficiency in the rigors of data analytics. Thirdly, Health Information Systems make the provision of healthcare fast and efficient (DiMatteo, 1998). A physician can access all the information they need to make decisions from one point. This increases their effectiveness.
Several questions arise from these issues. First, how are changes in the medical service provider models affecting the traditional and emerging roles of physicians? Is it possible that at some point, technology will replace the work of a physician? In this context, is it reasonable to assume that physicians must become more “tech-savvy” to survive in the modern healthcare setting? How much should a physician rely on decision support systems given that these systems use the aggregated information to provide support, while in reality, each patient has a unique medical history? These questions will inform the progress of this project.
Description
The research project will look at the roles of a physician from the perspective of the Dubai Hospital. The issues surrounding the use of the Health Information Systems in this hospital form the context of the study. By looking at the roles of a physician in the context of this hospital, the project will provide valuable insight into the posture physicians should take towards Health Information Systems. Many physicians do not get the opportunity to reflect on the role they play in healthcare institutions. They simply execute their mandate and move on. However, Health Information Systems will soon have a big impact on the role physicians play in the Dubai Hospital, hence it is important to examine all the contextual issues to better prepare for these changes.
The main benefits that will emanate from this study are that physicians will see that their place is changing in health institutions amidst the drive to implement different types of Health Information Systems, and they will have the information they need to adapt. However, this study may not answer all the important questions relating to these changing roles because of the unpredictability of the changes. What is important today may become insignificant tomorrow because of the sheer speed of technological changes. Information Technology brings about destructive changes whenever it is the principal driver of change. Health Information Systems expose the medical care industry to these forms of changes. One breakthrough in Information Technology may require an overhaul of existing systems in order to take advantage of new capabilities presented by the new technology.
Methodology
The study will require the use of three methods
- Questionnaires
A questionnaire will be the main data collection media for use in this study. The questionnaire will target physicians in order to determine their assessment of their roles within the Dubai hospital. The questionnaires will have open-ended questions and multiple-choice questions in order to extract both qualitative and quantitative data (Jacobs, Rapoport, & Jonsson, 2009). Principally, the main questions will have multiple choices while the supporting questions will have open-ended questions to provide an opportunity for the respondents to justify their choices. An email will be the mode of dispersal of the questionnaires. This decision comes from the understanding that it is easier to analyze data in electronic form. However, the use of email questionnaires will bring about data security concerns, hence the decision to make the responses anonymous (Holmes, 2005). Exemption from this rule will apply in cases where respondents prefer hard copies of the questionnaire. - Interviews, In order to validate information collected through the questionnaires, specific interviews with senior members of staff, senior physicians, and some of the questionnaire respondents, will take place. The interview with some of the questionnaire respondents will take the form of a focus group discussion in order to validate the data collected in the email questionnaires to clarify any unclear issues. On the other hand, interviews with senior administrators will take place on a one-to-one basis. These administrators have been with the hospital and in the medical industry for a long time hence, they are valuable resource persons. It will also be imperative to conduct one-on-one interviews with senior physicians to get a sense of perspective relating to the changes in the roles of physicians over time.
- System Evaluation
Finally, it will be important to map put the medical services system used by the hospital. This will include an analysis of the relationships that support the assigned roles of the physicians in the hospital. These relationships include peer-to-peer relationships, cross-functional relationships and relationships with external stakeholders. In addition, the system evaluation will map the use of Health Information Systems with an emphasis on systems that have a direct impact on the roles of physicians. There are several Health Information Systems in the hospital but physicians do not interact directly with some of them. It is imperative to look at these associations in order to understand the full impact of the operating environment, which includes human relationships and technological support systems, on the physician.
Results
Twenty-three percent of the respondents were female while seventy-seven of the respondents were male. The distribution of the respondents according to clinical positions included twenty doctors, five nurses, three pharmacists, and two lab technologists.
Roles Played by Physicians
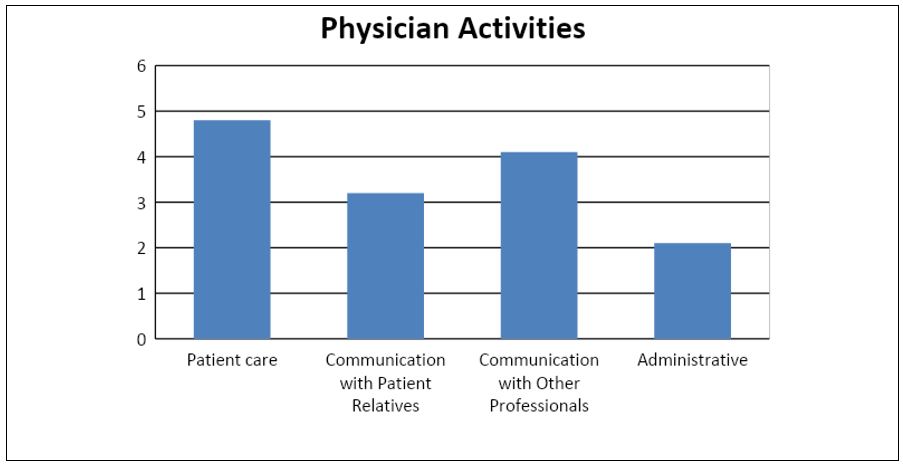
The main activity physicians take part in is patient care. This activity received a score of 4.8 out of 5. Communication with patients’ relatives and communication with other healthcare professionals scored 3.2 and 4.1 on the same scale.
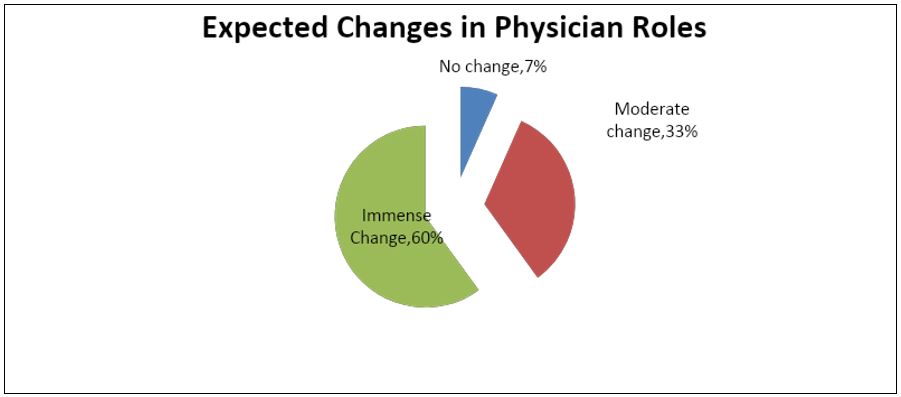
A third of the respondents felt that they were playing certain roles that someone else should be playing. Similarly, 77% of the respondents stated that the roles they are now playing were not part of the roles they anticipated to play during their training. When asked about their expectations of change in the roles physicians play, 60% of the respondents felt that in the next three to five years, the roles physicians play would undergo immense change. Thirty-three percent felt that the changes would be moderate while the rest did not expect any changes in the roles physicians play.
Bottlenecks Physicians Face in their Work
The most significant bottleneck that physicians face is working with IT equipment. The scores for this bottleneck averaged 4.2, which was the most significant bottleneck among the physicians.

However, 77% of the respondents felt that IT can help alleviate the bottlenecks in a physician’s line of work.
Current and Future Roles of Health Information Systems in the Work of Physicians
Sixty-three percent of the respondents felt that the use of Health Information Systems is justified. The number of respondents who felt that IT improved their performance outnumbered the respondents who felt otherwise as shown in Figure 4 below.
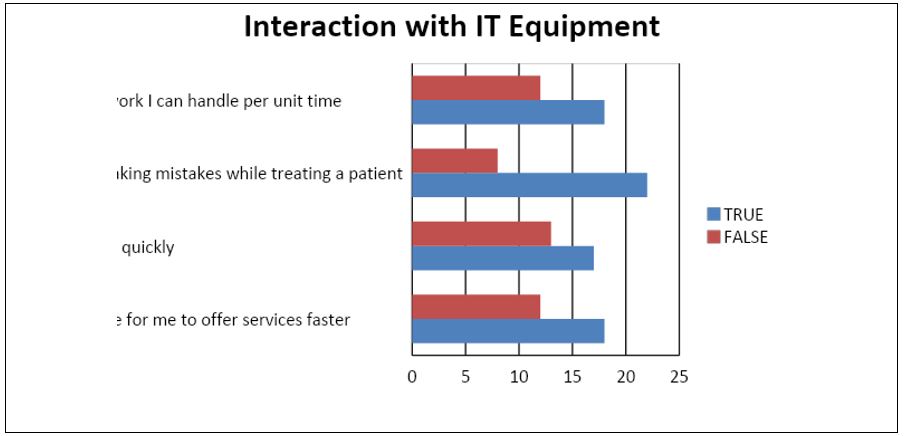
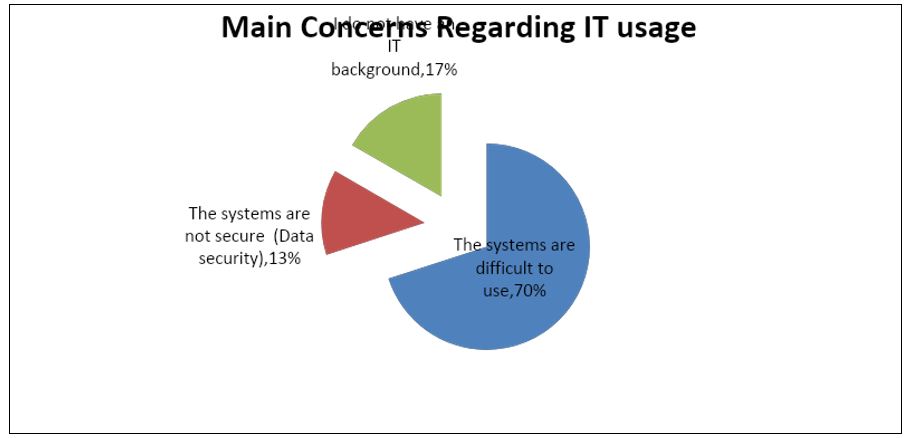
The most significant concern physicians have in regard to the use of IT systems is the usability of IT based medical systems.
Discussion
The findings from the research carried out correspond to some major trends affecting the practice of medicine. First, the findings show that one of the most demanding aspects of the work of a physician is communication. This is not apparent while examining the work of a physician. However, a closer look at the functions a physician plays reveals that it is impossible to carry out the duties of a physician without communication. The most fundamental aspect of communication is communication with patients. It contributes a lot towards the quality of service. A patient must feel that the physician has heard what is wrong with him or her to have confidence in the interventions the physician prescribes.
A second theme that permeates the role of physicians is changing. The roles physicians play will remain in a state of flux for a long time to come. Just as work processes in other industries are under constant change in response to new opportunities provided by technology and advances in operations management, the roles of physicians will keep on changing to take advantage of these advances. It is imperative for every physician to keep in mind that their training in medical school will not be sufficient to meet the demands of healthcare in the next decade. The rate of change will increase because of changes in information technology, and the advances in medical technology. Initiatives such as telemedicine, work process outsourcing and advances in medical technologies will change the operations of a physician in any part of the world.
It is important to observe that IT is becoming a core part of offering health services. While many healthcare providers outsource IT services, many of them are demanding more involvement of physicians in the use and management of IT systems. For instance, the adoption of electronic health records demands that physicians commit data to IT-based systems and not paper records. In addition, physicians should use these systems to retrieve information such as the medical history of a patient. In this sense, there is a need for all physicians to acquire a basic level of IT literacy simply to survive in the emerging healthcare environment.
Collaborative practice is also becoming an important trend in health services. Physicians are collaborative professionals that must work with other health professionals. They have a strong history of collaboration. The important trend in this aspect of healthcare is that technology will become more important under collaborative practice. There are gaps in the implementation of collaborative practice based on licensing limits. For instance, a doctor in India can participate in a surgical operation that is taking place in the UAE using telemedicine technology. This technological possibility may not work because the Indian doctor has no license to practice in the UAE.
Finally, the need for user-friendly IT services for physicians will increase as more physicians start to use IT services. Just like the field of medical engineering came up to provide engineering services suitable to the unique needs of healthcare, it is imperative to train IT professionals who can answer the unique IT needs of healthcare.
Conclusions
The significant conclusions arising from the analysis of the data include the following. First, the most significant role that physicians play in addition to patient care is communication. Physicians communicate to the family members of patients and to other healthcare professionals on a regular basis. Most physicians find themselves playing roles that are different from those they anticipated to play during their training. These changes are the result of the evolution of the medical industry partly due to technological advances. Indeed, many physicians are anticipating more changes in the coming years in the execution of their roles.
Many physicians reported difficulties working with IT equipment. This claim is not unique to this research project. Many physicians find it difficult to use Electronic Medical Records because of difficulties in accessing information from them. Each EMR vendor uses a different interface and menu arrangement. Therefore, a physician working in more than one hospital must take time to understand how each system works. Since physicians are not IT professionals, the interfaces make it more difficult for them to use the IT equipment.
The expectation that IT will become more dominant in the provision of healthcare and the acceptance of the value of computer-based systems by a critical mass of physicians is a good sign.
Recommendations
The recommendation for hospitals and other healthcare institutions is that they need to consider the roles that they need to play to make it easier for physicians to take up IT-based services. In reality, the use of EMR systems can slow down a physician if the system is not user-friendly.
Secondly, there is a need for IT companies that carry out EMR software development projects to create intuitive interfaces. This will ease the interaction of the physicians with the software. Such initiatives will improve the uptake of the EMR systems.
Limitations
The important limitations in this research project were the inability to construct a longitudinal study to measure the changes affecting the roles of physicians in hospitals over a longer period, and the limited range of issues that the project could address. The career of a physician goes through a number of changes that require long-term study to understand fully. It is impossible to single out one factor such as IT for study without regard to the other issues. The attitudes of a physician towards IT may be from the training of the professional in a non-IT environment. Physicians tend to be people-oriented. This orientation may hinder their acceptance of technological aids in the discharge of their duties.
References
DiMatteo, R. M. (1998). The Role of the Physician in the Emerging Healthcare Environment. Western Journal of Medicine, 168 (5), 328–333.
Hersh, W. R. (1995). The Electronic Medical Record: Promises and Problems. Journal of the American Society on Information Science, 772-776.
Holmes, D. (2005). Communication Theory: Media, Technology, and Society. London, UK: SAGE.
Jacobs, P., Rapoport, J., & Jonsson, E. (2009). Cost Containment and Efficiency in National Health Systems: A Global Comparison. Weinheim: Wiley Verlag.
Smelcer, J. B., Miller-Jacobs, H., & Kantrovich, L. (2009). Usability of Electronic Medical Records. Journal of Usability Studies, 70-84.
Ulmer, C. (2010). Future Directions for the National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Reports. Washington DC: National Academies Press.
Wittrup, R. D. (2007, March 13). The Changing Role of the Physician. Web.
Appendix
The Role of Health Information Systems in the Work of a Physician