Introduction
Background Information
The medical industry is one of the most important parts of society, and an incremental part of people’s lives, safeguarding their wellbeing and ensuring continued prosperity. The healthcare sphere is constantly changing and developing, creating better outcomes and solutions for problems present in modern times. Historically, modern technology has been widely used in this venue to improve the process of healthcare and healthcare delivery, allowing medical professionals to improve their approaches and reach a broader audience. With the spread of computer devices and the internet, possibilities for indirect interaction have expanded significantly, creating an opportunity for healthcare providers to develop beyond their regular scope of work. Telehealth as a concept has been employed by healthcare professionals for a number of years now, giving healthcare professionals the ability to better support the well-being of people. The use of computerized technology has long been adapted to medical practice, but the use of the internet as a vehicle for patient-doctor communication and healthcare delivery is still rather fresh. With the recent precedent set by the Covid-19 pandemic, the problem of interacting with patients indirectly is even more apparent, and the implementation of virtual visit technology is seen as an effective way of addressing the issue. To best counteract the effects of the pandemic and give people an ability to continuously prosper, the usage of telehealth is an absolute necessity. This paper will focus on discussing the benefits of a comprehensive change strategy involving the use of a virtual visit technology, and the benefits an AI-assisted program can bring to the hospital staff. The main issue of other approaches will be discussed, which will then transition to addressing the issue itself and the use and implementation of a continuous improvement strategy in the workplace.
The Main Issue
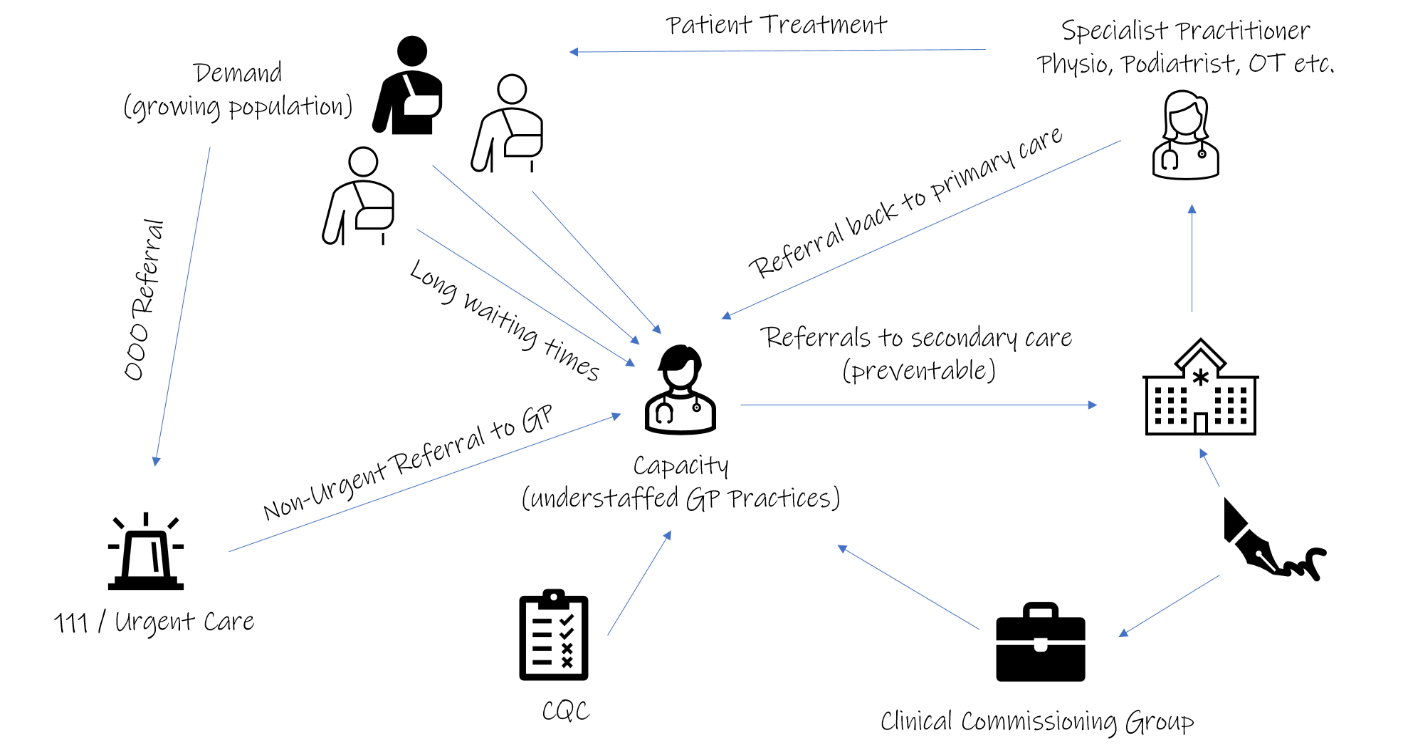
With the increasing population and the development of the online sphere, medical institutions seem partially unable to make use of the technology available to them for improving the healthcare process. Currently, the face-to-face systems of healthcare delivery are inefficient, as most hospitals are severely understaffed and overworked. Outpatient visits keep increasing, and the human resources of medical facilities struggle to meet the demand (Digital Health Solutions, 2020). It is noted that at least 43% percent of all outpatient visits can be fully relegated to the digital sphere, which would significantly reduce the overuse of waiting rooms and alleviate stress on healthcare workers (Digital Health Solutions, 2020). The inability to answer growing demand creates longer delays and decreases the quality of care given to patients. The system of engaging with hospital staff directly also involves a variety of components, many of which slow down the procedures considerably and contribute to staff exhaustion. The biggest portion of the patient influx is put on primary care workers, that have to manage the treatment of patients or redirect them to specialists, which takes up both time and resources. The reliance on primary care doctors as the center of medical operation puts an unnecessary strain on overworked staff and makes the process of healthcare more inefficient. Furthermore, due to the need for in-person visitation, a sizeable portion of the population has difficulty or is wholly unable to receive medical support. It can be noted that at least 56% percent of people cannot visit a hospital in-person due to their physical distance from available healthcare (Digital Health Solutions, 2020). People with health complications, who live in remote areas, and others are underserved under the outpatient-oriented system.
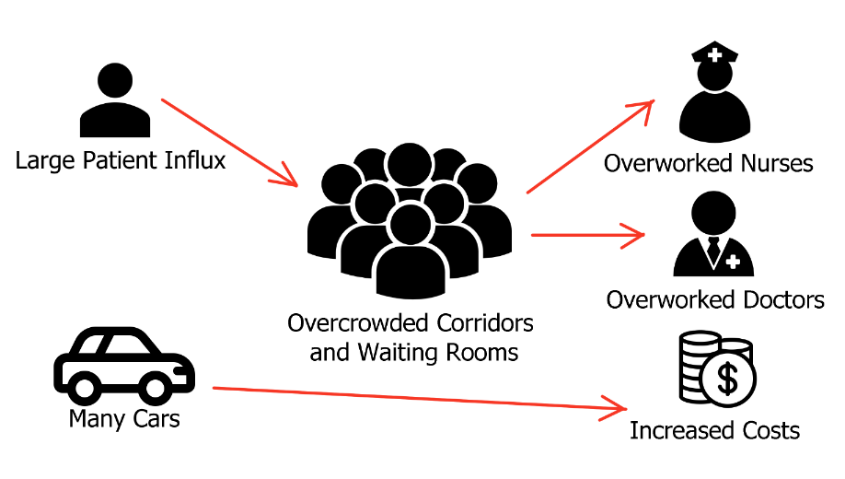
These two figures highlight the main problems of the traditional healthcare delivery system, and the issues that a virtual visit application can address. In-person visits largely depend on the ability of doctors to quickly and effectively tend to patients, fill out paperwork and conduct examinations, which is becoming increasingly hard due to a variety of factors. A large amount of people in waiting rooms and corridors increases expenses spent on maintaining a hospital and worktime, therefore decreasing the efficiency of medical work and costs.
An approach that would give people the ability to consult with a doctor indirectly would decrease the concurrent workload of primary doctors and allow a bigger portion of the population a direct way to access healthcare.
Another issue that significantly increases the need to introduce an alternative to in-person visitation is the emergence of the recent Covid-19 pandemic. The extremely contagious Coronavirus has forced all aspects of human society to adopt protective measures and impose particular restrictions on people’s ability to reside in public spaces. Hospital waiting rooms are an especially potent source of worry, as they put people in close proximity to each other, often for prolonged periods of time. The need to schedule and wait for an appointment, as well as to personally interact with others puts many at significant risk. This is especially dangerous because many patients have pre-existing conditions that endanger their health and wellbeing. The need to ensure public safety prompts healthcare institutions to find ways of reducing the patient load and redirecting a bigger portion of direct visits to the virtual sphere.
The Aim and Objectives of the Study
The main aim of this study is to aid healthcare workers in adapting to the changing environment of today and addressing the issues of high priority. A healthcare delivery system weakened by the pandemic and an ever-increasing influx of patients has to develop a way of fulfilling the needs of the many whiles also taking staff satisfaction into account. Currently, the staff are often forced to work overtime and do not have the ability to promptly help all the patients receive medical care. A system of online interactions can serve as a proxy for an in-person visit and make the organizational elements of medical work faster. The paper will introduce, contextualize and discuss the implementation of a virtual visit application for healthcare institutions. In particular, the study will attempt to understand the main issues connected with the healthcare of the 21st century and the implementation of an internet-reliant healthcare system, its challenges, work strategies, and challenges faced in the process. All of the information and research presented are applied in an effort of using modern technology to improve healthcare delivery, patient-doctor communication, and the efficiency of the work environment. The introduction of a virtual visit system will hopefully revitalize the stagnant healthcare sphere, lessen the doctor’s daily workload and address the need for better adaptability to the current pandemic.
Addressing the Issue
Root Causes of the Problem
To better understand the root causes of the issues that will be solved by the application, one can use the 5 whys approach. It allows individuals and teams to critically assess the cause-and-effect relationship between the biggest issues and some of the problems a healthcare institution may have.
“Why is the waiting time in hospitals so high?”
It is a well-known fact that waiting times are one of the biggest current causes of concern, for both the clientele and the medical staff alike. Current research shows that, on average, a person has to wait for around 6 days before getting an appointment with a doctor, and a usual hospital visit takes up to 121 minutes (Digital Health Solutions, 2020). The time lost on transportation, waiting, and the process of having an appointment considerably strains the medical system, and wastes a large portion of its funding. With a constant supply of new patients, the shrinking medical staff is becoming increasingly less efficient, and precious hours that could be used to save lives are wasted. Doctors cannot give people access to quick healthcare during in-patient visits while also ensuring its quality.
“Why are medical staff unable to meet patient demand effectively”
Hospitals and other medical institutions are constantly facing the problem of overcrowded waiting rooms. The demand for healthcare and medical attention is simply too high for the number of people currently working in healthcare to answer in person. The process of scheduling an appointment, waiting in the queue, and receiving care takes up a considerable amount of time, and the more hours spent on each patient, the slower the whole process gets.
“Why is the number of patients so high?”
People requiring urgent medical attention and direct intervention are coupled with those that do not require such drastic measures, unnecessarily stressing the healthcare system. In-person visitation is often seen as the only viable way of receiving healthcare, which damages the system as a whole and makes it less effective at assisting people. As noted before, at least 43% of all outpatient visits can be fully relegated to the digital sphere without affecting the quality of care.
“Why do people unnecessarily perform in-patient visits?”
This issue stems from the lack of variety in the available ways of receiving healthcare. Such volumes as cough, flu, fever, skin rash, back pain, and similar do not require a person to visit a hospital to receive support, yet, they tend to go in person regardless, endangering themselves and others. Alternatives for a traditional hospital visit do not always exist, and seem inaccessible or unreliable, creating a bigger systematic issue in healthcare.
“Why is there no alternative ways of accessing healthcare?”
Many hospitals and medical care facilities see the prospect of a virtual visit application as achievable or ineffective. Systems of quickly delivering health care through the Internet and online communication exist, but they are not universally adopted, making the practice less effective than it could have been.
Overall, it can be noted that a strong incentive exists to create a virtual visit program two effectively address the need to engage with larger amounts of people quickly. the growing number of patients and the potential prospects for saving time, money, and human resources is a Huge incentive for going forward with a virtual visit application. As the five whys analysis suggests, the most pressing issues in the health care industry stem primarily from overcrowding and unnecessary in-person visits that can be shifted to the online sphere.
SWOT Analysis
Another effective way of understanding the implementation and use of a virtual visit application in regard to healthcare is a SWOT analysis. A tool made to analyze a particular organization’s strong and weak sides can provide a significant advantage when trying to introduce a new strategy.
Resolving the Problem
As surmised in the previous paragraph, the main issue that this project aims to address is the lack of choice in inpatient hospital visits and the critical overcrowding of medical institutions. A virtual visit system would allow healthcare professionals and healthcare delivery services to better support the needs of the many and comply with the current regulations set upon by the COVID-19 pandemic. The use of online virtual visits as a means of communication between the patients and the doctors can significantly reduce waiting times, make the process of continued support easier, and facilitate convenience for both parties.
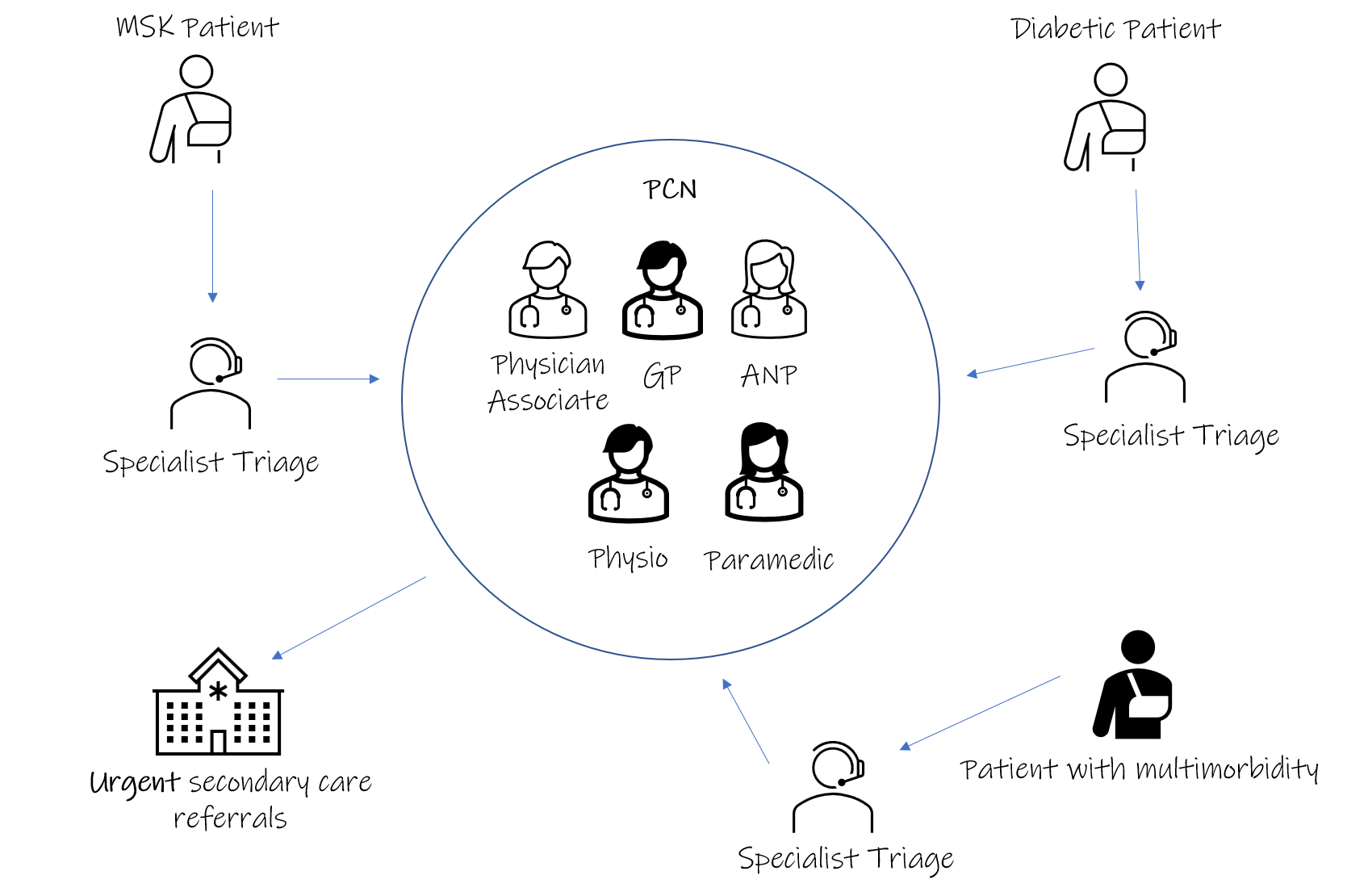
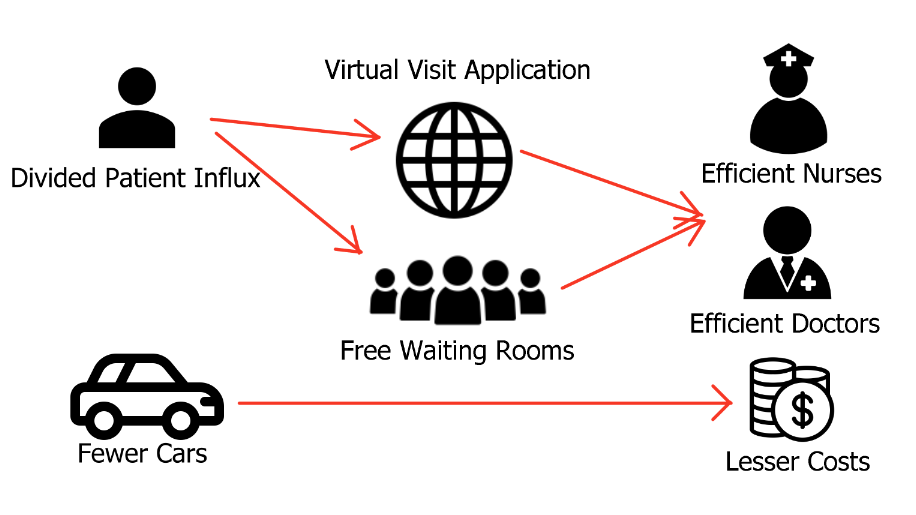
As shown by current research, 73% of patients agree with the notion that virtual care improves the accessibility of care and the speed of initiating treatment, and satisfaction rates while using virtual visits were further improved by 97% (Digital Health Solutions, 2020). Those not requiring urgent care or direct intervention will have the ability to get faster and more convenient access to doctors, and the people that need medical attention will have a quicker pathway to it. Virtual visit systems allow for customized approaches to each patient, and a schedule that is convenient for all parties involved. Those in need of an in-person visit will also enjoy the benefits of making appointments easy, with an ability to actively monitor the availability of a particular specialist.
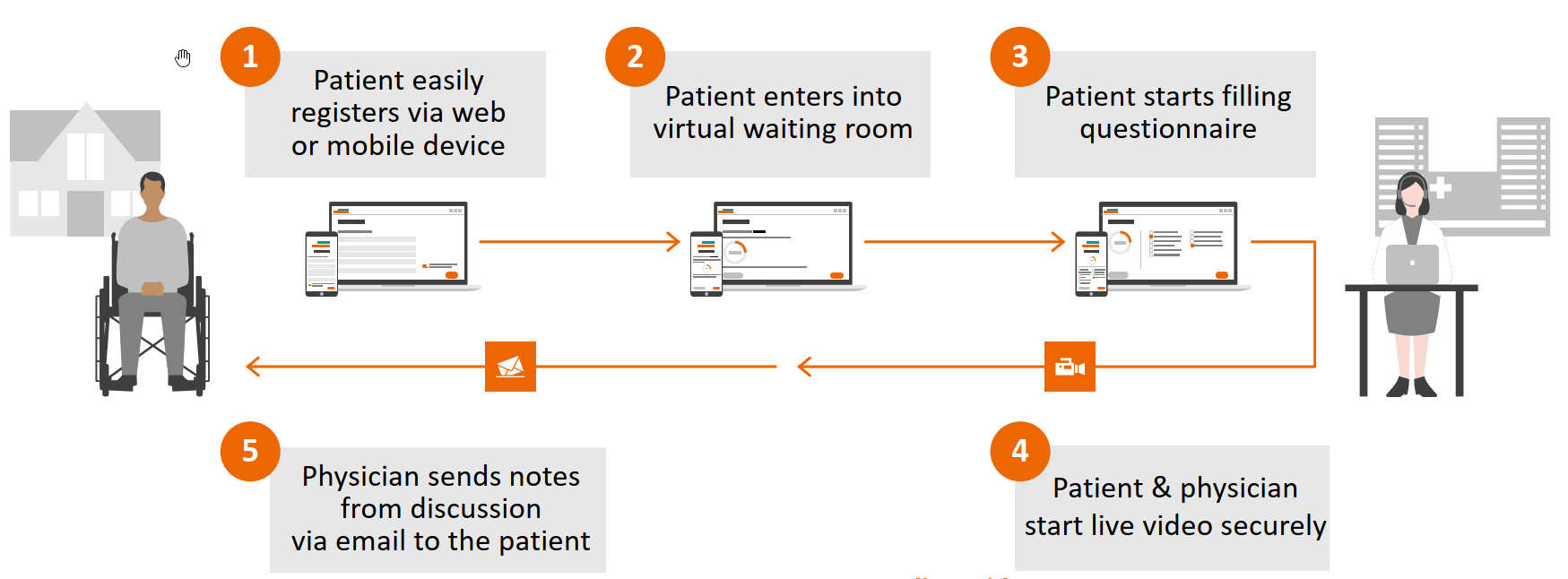
The above figure represents a general flow of an appointment with a doctor using the virtual visit application. The process is made to be intuitively understandable and requires a few steps to complete. Registration is accomplished via a desktop or mobile website and using their data the patient enters into a virtual waiting room. While on the waitlist, they can fill out a questionnaire that gives medical professionals the ability to quickly gather the most essential data and shorten the time required for an appointment. The meeting between the two parties then occurs over video conference, with security and patient comfort taken into account. After the appointment is completed, the patients remain interconnected with their doctors and are able to receive notes from the discussion. This system promotes patient agency, connectivity, interactivity and faster hospital interactions.
The Plan and Purpose of the Change Strategy
An introduction of a comprehensive system for making online appointments and communicating with doctors is to be created. The virtual visit platform will be empowered by the combined work of healthcare professionals, technicians, operators, and modern AI technology, in an effort to make it deliver good results. Patients will be able to register and submit their medical data for assessment by doctors, schedule online appointments and receive prompt support throughout the course of their recovery. Once the program is established, its main benefits and effects need to be evaluated, as well as the overall influence it has on staff productivity, satisfaction, and patient outcomes. The extensive analysis will allow the medical institution to acquire a thorough look into how the application functions, the ways of improving it, and the potential areas of development. As for the effectiveness of the potential implementation, most sources state that the usage of telemedicine and virtual applications is highly dependent on the quality of its implementation.
Change Strategy
Implementing a virtual visit program is a gradual and continuous process, requiring constant change and evaluation to be effective. The virtual visit program will include a framework for interaction between the patients and doctors, and communication over video, audio, and text. In essence, users will be able to register for an online service and participate in an online waiting room. While waiting, the applicants will have the ability to fill out forms and questionnaires concerning the reasons behind their visit, and the type of assistance they will require. Once their time has come, a doctor will see them from the comfort of their home, via a video call. The patients will also be able to get specific appointments, send their data over secure channels, and establish a sense of connection with the medical professionals. Most importantly, the system has to promote a sense of personal agency, choice, convenience, and control. Allowing patients to choose the time, place and preferred method of communication gives the process of medical care an accessible front, one that will be beneficial to developing a healthy relationship between healthcare providers and their clients. After the appointment is finished, the process of monitoring patient progress becomes more efficient for the medical staff. The practice not only eliminates the need for in-person visitation in many cases but also ensures that more people actually show up to their appointment. On the topic of appointments, the use of an online application prevents loss of time due to lateness thanks to cutting out the need for transportation and reducing the time spent on each individual person. The managerial and organizational aspects of the process are more easily covered by patients filling out forms, and questionnaires that give the medical staff faster access to data. The use and success of the program will be measured through accessing the available data with change models and gathering patient feedback to further improve the service.
Change Models and their Appliance to Change Management
McKinsey 7-S Change Management Model
The 7-S model will be applied to the process of implementing a virtual visit program in an attempt to understand how its introduction will change the core aspects of the medical institution. Because of the need to form a cohesive and effective virtual visit program that will be compatible with the contemporary work of a hospital and innovative to its operation, the 7S method is especially relevant. It allows one to look at the founding components of an organization, and understand how they influence each other, and the ideology that supports them. The model recognizes 7 different elements of an organization, 3 hard elements, and 4 soft elements. Hard elements are easily defined and can be changed by the direct intervention of the management staff. Soft elements, on the other hand, are influenced by the former and are shaped by the company’s operation and culture. They are less accurately defined with concrete terms and measurements but are nevertheless crucial to an organization’s operation. An evaluation and change of an organization, as well as the introduction of change, starts from examining its shared values, as they are the thing that underlines most major decisions made in an organization.
Table 2: Elements of the 7S Framework
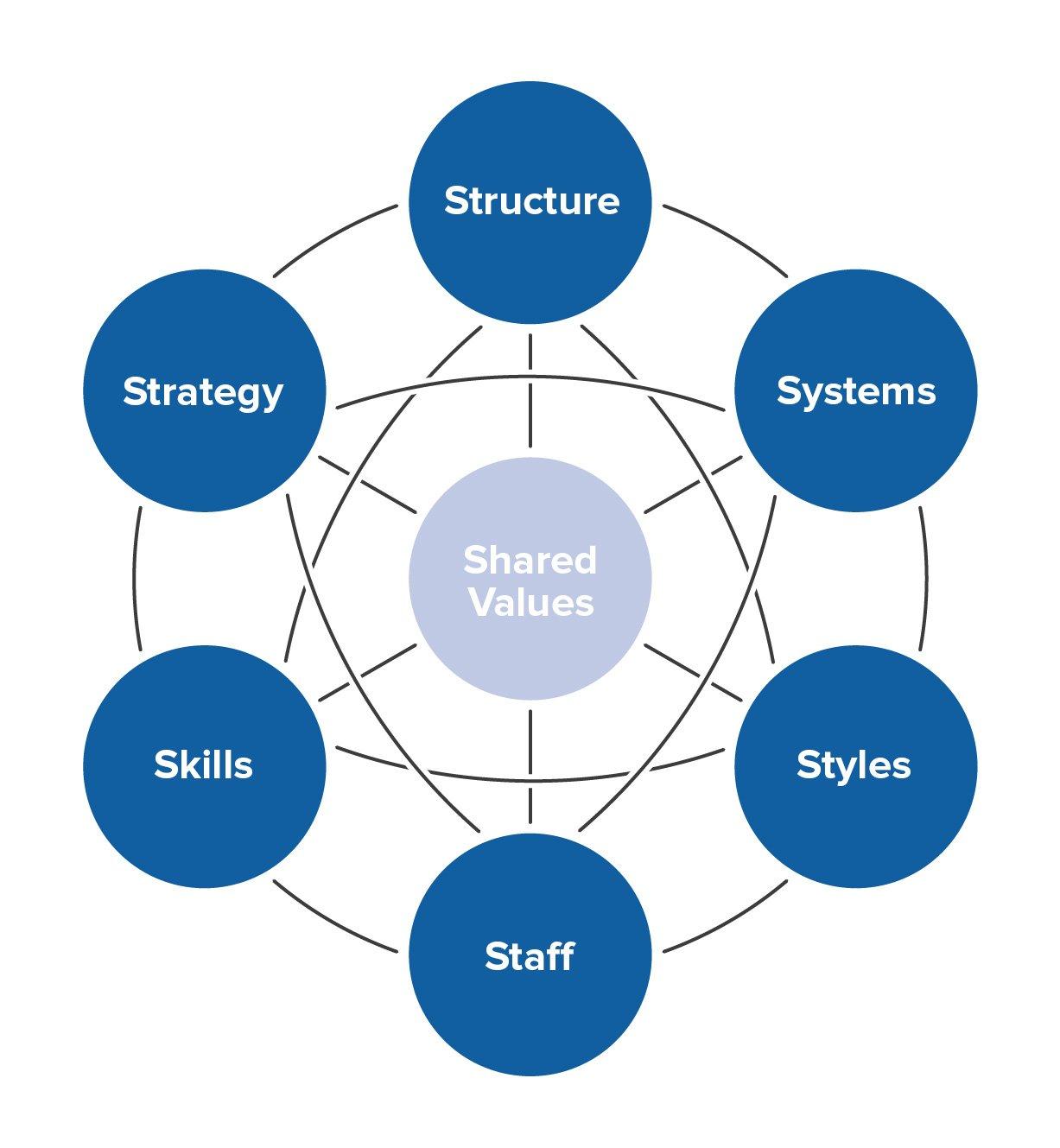
The model can be used to access both the state of a hospital before and after the implementation of change (Mind Tools). An evaluation will be useful in accessing the main benefits of the changes made, the specific parts of the hospital organization they will affect, and having a basis for measuring the success of the implementation itself.
Shared Values
The core values of any healthcare organization include ensuring the safety and continued wellbeing of patients, providing healthcare that complies with contemporary standards of care, and contributing to the wellness of its general community. Effectively allowing the staff to work in conditions that are welcoming and secure, giving potential for development and self-actualization. Personal and professional convenience for patients and workers respectively is also a big consideration, as an efficient organization is a key to wellness. These values are what drive the practice and management of healthcare organizations, and precisely what should take priority during the implementation of change. By comparing the current state of affairs to the potential benefits a virtual visit application could bring to realizing these values, one can decide which aspects of implementation are most important.
Strategy
The strategy of the hospital involves providing individuals with affordable healthcare, monitoring their wellness, and finding ways of adapting medical knowledge and new skills into active practice. The process of continued development and growth is the core of the operation, which ensures that medical professionals are able to accurately secure the health of the population. Hospitals work together with a variety of partners, including specialized care providers, suppliers, and community programs, in an effort to realize their core values in practice
The use of a virtual visit application, therefore, is a natural extension of the current strategies medical institution may utilize. Using modern technology to bring comfort, convenience, and assistance to those that need it, transforming theory into practice and engaging in constant evaluation of patient health. By implementing the telehealth approach, hospitals are able to further adapt their services to the changing environment of today.
Structure
The organizational structure of hospitals and healthcare facilities is a complicated web of interactions and evaluations aimed at providing clients with improved health outcomes. The work is aligned around this general trend, with each specialist being responsible for their own part of the process. The relegation of tasks helps keep track of operations and employ specialists in their particular sphere.
Implementation of a Virtual Visit application further supports this basic structure and alleviates some of the pressure from working with a large number of people. The treatment of patients is completed through the combined efforts of healthcare specialists, technical staff that maintain the service, and the active operators that help with management aspects. The use of team labor to achieve needed outcomes coincides with the overall structure of hospital work.
Systems
Hospital operation in terms of healthcare services primarily relies on two systems: the management and the actual doctors that work directly with patients. By finding convenient methods of organization, increasing work efficiency, and regulating the practices of healthcare workers, the management has the ability to ensure that the process of healthcare is being performed on a sufficient level.
On an online platform, similarly, work will be handled by both organizational staff and those that work directly with patients. Gathering data, ensuring that records are stored safely and are easily assessable to doctors, and making the process of finding a needed healthcare professional more efficient, management and various staff from the system of healthcare delivery. The implementation of an online application works towards dissipating the patient flow and making the general organizational efforts more effective.
Skills
A variety of skills are presented in a hospital setting, many of them connected with the need to work with patients. Confident communication, and an ability to understand and establish an emotional connection is crucial as it is what allow medical workers to get information from their clients. An ability to ensure patient wellness, perform medical examinations and accurately evaluate a patient’s condition, as well as the skill of making well-informed judgments are all displayed by doctors and other medical professionals.
In a virtual visit application, many of these skills are further utilized, as doctors need to perform examinations and work with patients. However, a need to adopt new strategies for interaction and work skills is also critical. Using the online sphere in an efficient manner, performing medical work remotely, and continuously engaging with patients on an indirect basis are all skills that need to be adapted into constant practice.
Style
Generally, cooperation between different parts of a medical facility and between staff is what drives healthcare practice forward. By promoting an active dialogue and engaging with each other, doctors and healthcare workers gain the ability to work together as a team and learn from each other’s experiences.
The process of cooperation is also much needed in implementing a virtual visit application, as the use of modern technology is often difficult to fully adapt to. By sharing useful tactics and working together, hospital staff can effectively improve the standards of care and utilize the new resources available to them.
Staff
Hospital staff is varied and diverse, having to fulfill a variety of roles to successfully align with the common values of healthcare workers. Doctors, nurses, managerial staff, team leaders, and major stakeholders, all work in accordance with the current medical research to play their role in the community. The competencies are varied as well, including professionals in staffing, communication, healthcare, hr, organization, and many other niches.
The virtual visit setting will utilize a variety of existing staff positions and their competencies, as well as procure a need for new types of knowledge to be utilized. The technical aspects of implementing an online application, especially, will require changes in staffing.
From this evaluation, it can be said that the use of a virtual visit application aligns with the needs, values, and abilities of a healthcare organization quite well, requiring limited additional changes to be fully realizable and effective. By promoting more tech-oriented competencies, healthcare organizations can have an opportunity to more fully actualize their values of promoting patient and staff wellness.
Staff Behavior Before/During/After the Change Strategy
Staff attitudes and behavior is an inherently crucial part of introducing the virtual visit application, as they are the ones that are responsible for working within the online framework and continuously improving the quality of the new approaches. Leadership and management are of utmost importance during the implementation and improvement effort and should be the primary concern in the process. Management organizes the work of other employees, gives them an ability to focus on their own specific tasks and effectively cooperate in stressful and changing circumstances. Bold and thoughtful management is what allows medical organizations to quickly utilize the newest technology and strategy in the workplace. Leadership, similarly, works for the continued improvement in the workplace, and its ability to face challenges ahead. Leaders are able to set manageable goals, direct action, and decide when to change the direction of the change strategy. In the period before the change strategy is implemented, the staff should be surveyed for valuable feedback on the implementation and features of the virtual visit program, as well as the reception of its adoption in the hospital. This would allow the management to better understand the general attitudes towards the use of the virtual visit system, main points of contention, potential areas of improvement, and aspects that require deeper analysis in the future.
During the implementation of the virtual visit program, a part of the medical staff should be assigned to work within it and be properly educated on engaging with patients on the basis of an online platform, as well as proper ways of organizing work-related data in a new environment. The initial adaptation phase of the process should also be accompanied by a continued collection of worker feedback, and possible changes in the project should be made in accordance with it. After the implementation of the framework is complete, an evaluation of staff engagement with the adopted improvement should be made using available methods, and measures including further coaching should be used to eliminate misunderstandings.
Lessons Learned, Outcomes
The implementation and use of virtual visit programs can give health care institutions and hospitals and ability to gather precious experience that can be used to further inform future practice. The staff will be able to learn ways of interacting with patients from a distance, building engagement and connection via video, text, and phone calls, as well as aid a more significant number of individuals. The utilization of the virtual visit application will have long-reaching implications in the sphere of health care and can open a file for better accessibility in the field. important cementing the change strategy hospital management and doctors can find ways of optimizing their workload organizing digital records and holding online appointments. Overall, the process of using a virtual visit application will not only be beneficial to patients but also to the growth and development of the healthcare sphere. it is expected that the implementation of the program will lead to better healthcare outcomes for many patients including faster recovery time, decreased frequency of accidents, and established confidence in online health care. the practice is also expected to disincentivize people from missing their appointments and reduce potential lateness.
Continuous Improvement Strategy
Projected Outcomes
Outcomes for the implementation of this program include a variety of improvements to the operation of the hospital. It is expected that the efficiency of healthcare delivery will be increased, as well as the speed of patient appointments. This will be possible by reducing the pressure put on the medical staff and decreasing the amount of in-person visits the hospital receives. The revenue is expected to see an increase, while the costs are likely to fall significantly. Due to the changes in service delivery by using the virtual visit system, a portion of the cost will be avoided. The use of the new system is also projected to increase patient and staff satisfaction and contribute to lower levels of stress, overwork, and anxiety. Effectiveness is projected to be increased in a variety of ways, including the quality of operation and increased reach of healthcare efforts. In terms of enhancing the quality of care, the use of an online application will be beneficial to patient monitoring, continued assistance, and the improvement of patient-doctor communication. Organizational improvements will also be evident, as the operation of a medical institution will be less reliant on primary care physicians as an intermediary between the patient flow and care. The delegation of care to the digital sphere is expected to create an alternative avenue to make addressing the daily tasks of a hospital easier. Most importantly for the current world climate and the global pandemic every institution needs to adapt to, the implementation and use of a virtual visit system are expected to improve preventive behaviors and better support the need for following the government regulations.
Tools For Measuring Success
Six Stigma
Six Sigma is an approach that is useful in both improving existing strategies of an organization and introducing new frameworks. The main focus of the method is on the facilitation of a continued, full system of improvement that is adaptable to the contemporary environment and adaptable to emerging circumstances. It helps organizations and companies to eliminate faults and provide better services. For the purposes of improving the healthcare delivery process, a DMAIC method of Six Sigma can be applied.
D – Stands for defining the problem, and recognizing the goals of the project. In the case of the virtual visit application, the main problems can be recognized as the inability to properly abide by Covid-19 restrictions and limited access to people with special needs. The goals of implementing change would be, among others, to decrease time spent in the waiting rooms, improve work efficiency and improve the communication channels between patients and doctors.
M – Means measuring the aspects of the current process. Currently, the healthcare delivery process relies on primary healthcare providers to directly interact with patients and provide care.
A – Is responsible for analysis as a way to find root defects in the current approach. The root problem with the traditional healthcare delivery system is that doctors are less capable of efficiently and effectively treating patients, and the patients are exposed to the risk of Covid-19 infection due to close proximity to each other in waiting rooms.
I – Signifies improvement, the introduction of a different approach to the business process. The virtual visit program introduces an effective and convenient way for doctors and patients to interact. Through the use of the internet, care can be provided remotely, expanding the possible range of patients and giving healthcare providers better connectivity to clients.
C – This is the final part of the method, and stands for controlling how the process will be maintained and evaluated in the future. The virtual visit framework will be continuously evaluated on its ability to bring systematic and individual benefits to the staff and patients by applying various improvement measurement frameworks and the collection of patient data.
Quality Improvement Measurement Framework
In terms of measuring the success of the virtual visit program and its implementation, one can refer to the framework introduced in the article “Defining and Assessing Quality Improvement Outcomes: A Framework for Public Health” (McLees et al., 2015). The research presents an evidence-based approach to assessing the quality of improvements in the public health sector. Authors have designed their approach in accordance with the main needs of the public sectors and the points of interest concerning improving employee satisfaction and patient outcomes (McLees et al., 2015). The framework is effective at addressing the potential benefits of implementing a virtual visit system due to being developed as a standardized measure of evaluating healthcare sector quality improvements. The study bases its review on two main measures – efficiency and effectiveness, as the two are seen as the key foundational aspects of quality improvement (McLees et al., 2015). The criteria were chosen for their wide applicability and relevance.
Table 3: Quality Improvement Framework
Final Outcome
The final outcome of the implementation of the Virtual Visit program would be the ability to better achieve a variety of goals set by a hospital or healthcare organization. The current healthcare approaches are not adequately able to handle the patient influx connected with big city populations and the circumstances of the Covid-19 pandemic. The use of a virtual visit application allows healthcare providers and patients to collectively improve the healthcare experience, enhance communication and introduce a system of continuous development. The use of a virtual visit framework aligns with the major values of healthcare organizations, including the need to prioritize patient satisfaction, safety, and health. The use of an online sphere allows healthcare professionals to reduce the burden of having to examine each patient in person and places a number of intermediary mechanisms that make the process of receiving care more efficient. The use of virtual visits contributes to better medical practice, improves overall convenience, and paves the way for the use of modern technology, AI, and the internet in healthcare delivery. Proper implementation of the program has major positive implications for healthcare organizations and increases the profitability of work while significantly reducing costs. Most importantly for the current year, it helps healthcare providers to better work within the constraints of the Covid-19 pandemic by reducing the amount of direct contact experienced by both the staff and their clients. Hospitals using virtual visit programs can provide assistance, evaluation, and monitoring to people staying in-home, and those in remote locations. Overall, the use of modern technology, and the virtual visit framework specifically help healthcare providers to better assist people in their continued prosperity.
Conclusion
In closing, this paper has introduced the concept of a virtual visit application as a relevant and valuable solution to the problems faced by the healthcare industry. The use of a virtual visit program can be beneficial to both the patients and the staff, as it contributes to decreasing hospital crowding and improving the accessibility of health care services. During the time of the Covid-19 pandemic, the question of keeping people from public spaces is more relevant than ever and the use of an online-based platform is one of the best ways of eliminating the need for gathering people in one place. the virtual visit application has been evaluated by a variety of frameworks discussing its primary methods of operation and its benefits for the hospital staff and for the patients. The 7-S has been used to identify the main components of a healthcare organization, and how they align with the improvements introduced by the virtual visit program. A Six Sigma approach has also been utilized to decide on how to best implement the strategy, and the particular steps that need to be taken to integrate within the hospitals’ operation. A standard Quality Improvement Measurement Framework has also been utilized as a way to measure the continued success and usability of the application.
Reflection
The final project paper has been an immensely interesting and complex work to take on. While some of its aspects were more difficult to take grasp, others were more inherent and instinctual which allowed me to hold a relatively smooth flow of thought throughout the paper. I have attempted to utilize different frameworks to analyze the application of the virtual visit program and demonstrate why I think it is an effective way of improving the workflow of the hospital in the current circumstances. The evaluations focused on providing a convincing basis on why the online application should be used and how it can contribute to reaching the main goals the medical setting sets for itself. I feel that the use of a virtual visit application effectively reaches a balance between introducing new concepts and meeting the contemporary goals of the health care organization. Working on this paper allowed me to practice and develop a variety of skills, including the synthesis of information, formulation of my own thoughts, and complex analysis of specific subjects. I feel that I can use many of the skills obtained throughout this work in my future research, and as a way to better understand what components comprise an improvement strategy in an organization.
Reference List
McLees, A.W. et al., 2015. Defining and Assessing Quality Improvement Outcomes: A Framework for Public Health. American Journal of Public Health, 105(S2).
Mind Tools, The McKinsey 7-S Framework: – Making Every Part of Your Organization Work in Harmony. The McKinsey 7S Framework. Web.
Digital Health Solutions (2020). ‘eHealth Virtual Visit’ [PowerPoint presentation].