Introduction
Management is the effective coordination of the resources of an organization towards the achievements of the goals and objectives of the respective company or organization. There are several organizations in the global industry but competing for limited resources. This requires an effective management team. Although management is important in the running and coordination of functions of businesses, leadership is also equally important. Effective leadership and management skills are required for increased efficiency and smooth management of the functions of an organization. The business environment is dynamic and frequently changes, which requires an effective human resource team to respond to the respective changes promptly (Baulcomb 279).
In an organization, initiated changes aim to enhance efficiency or respond to changes in the business environment that affects the operation of the respective organization. The health care industry is one of the most dynamic in the global industry. Several changes affect operation in the health care industry that requires a prompt response to ensure efficiency in operation. Technology affects operations in most organizations globally; it has also affected the way of operating in the health care sector. Technological use in the health care sector enables healthcare organizations to centralize their operations and increase efficiency in operation. Centralization of operations is a strategy used by most organizations to increase efficiency in operation (Bartholomew). Decentralization of operations is expensive and affects the quality of operation in most organizations in the global economy. Centralization enables an organization to easily monitor and evaluate its operations. It also enables an organization to review the progress of projects within the organization regularly. Companies, businesses, and organizations initiate projects to aid in the achievements of the goals and objectives of the respective company or organization (Butler, Boxer, and Sutherland-Fraser 11).
The dynamic nature of the business environment compels organizations to change their ways of operations. This has led to the introduction of the centralized system of operation within an organization. Organizations require strategies and models to respond to the dynamic nature of the business environment. Management specialists have developed different strategies and models of change, but they address different needs of an organization. Adoption and application of the strategies depend on the needs of the respective organization. This is an application paper on the centralization of laboratory information through the application of the Health Service Executive model (Bhalla, Aron, and Donskey). The Health Service Executive model is one of the most effective models, which organizations in the health care industry use to enhance efficiency in operation. Moreover, the model is effective in the establishment of programs that improve and enhance the quality of services offered by a health care organization. Health care organizations require effective strategies and models that increase efficiency in operation (Calms and Shusterich 11).
Increasing efficiency in operation is a dream that most organizations have. Increased efficiency in operations enables an organization to achieve its goals and objectives within the stated deadline or period and successfully implement its projects within a portfolio. Organizations operate to make profits. However, the maximization of profits within an organization is challenging due to the dynamic nature of the business environment. This has compelled several organizations to change their operational strategies to enhance returns levels (Abdel-Galil). Organizations change their ways of operations to increase efficiency in operation, increase the levels of returns and gain a competitive advantage in the industry and the global economy. However, employees due to several reasons resist change in most organizations. Therefore, an organization should choose an effective change model, which enables them to successfully introduce and implement change. This paper discusses the centralization of laboratory information within an organization through the introduction and implementation of the Health Service Executive model. The health service model is effectively implemented in an organization in conjunction with the implementation of the Project Portfolio Management System (Christian 163).
Aims of the project
This is a project-based on leadership and management in the health care industry. The project aims at increasing efficiency in a health care organization through the introduction and implementation of the Health Service Executive model. Generally, the model will be used to aid in the centralization of information in the laboratory department, which is a program that increases efficiency in operation.
Objectives of the project
- Centralization of laboratory information in the organization
- Enhancing pre and analysis of specimens in the department
- Enhancing collection of information within the organization
- Enhancing the flow of information within the organization
- Increasing efficiency within the department
- Increasing efficiency in operation within the organization
Literature review
There are several organizations in the health care industry. This has led to increased and intense competition, which has also contributed to the emergence of models and strategies used in enhancing and improving the quality of services within organizations. A health organization has different departments, which work towards achieving the goals and objectives of the respective organization. Achievement of the goals and objectives of an organization depends on the effectiveness of departments, employees, and the management team (Jeffries and McClean). Health care organizations deliver services to clients but face challenges of effective and efficient delivery. The laboratory department works on several projects; therefore, managing the multiple projects within the department and the organization, in general, is challenging and has affected the achievements of the overall goals and objectives of an organization.
Health care organizations have different departments, and each is responsible for the execution of different projects, which aim at the achievement of the overall goals and objectives of respective organizations. Organizations have been distributing projects equally among departments based on the nature and functions conducted by individual departments (Becker and Douglas). The projects’ completion contributes to the achievements of the overall goals and objectives of an organization. Individual departments’ operations should ensure the achievement of departmental projects, goals, and objectives because they contribute to the achievements of the overall goals and objectives of an organization. Furthermore, individual departments, for instance, the laboratory have different sub-departments, which execute different functions. Coordination of these functions in case the operations of an organization are decentralized is difficult and affects the operation of most organizations (Abdel-Galil 397).
There are several resources that organizations require to achieve their goals and objectives. However, human resources are the most important resource within an organization. It is the duty of human resources to develop, and implement strategies that will lead to the achievement of goals and objectives of an organization. Furthermore, it is the duty of human resources to develop realistic goals and objectives within an organization. Implementation of these strategies requires an effective and competent human resource team. Health care organizations require programs that improve the quality of services to customers and operations. Service provision is the function of health care organizations (Wiegmann, ElBardissi, and Parker). The laboratory is the main area of operation in health care organizations. The department is concerned with the collection, analysis, and presentation of clients’ data within the organization. Furthermore, the department requires an effective and competent human resource team to ensure efficiency in operation (Braaf, Manias, and Riley 1).
Several health care organizations face challenges in the coordination of functions in the laboratory department. Health care organizations require specialized, competent, and qualified employees in the department to assist in the operations and successful completion of duties and responsibilities within the laboratory department. There are certain data that require a prompt response, but organizations cannot promptly respond to them due to the nature of operations and functions within the department (Barcombe). Furthermore, most health care organizations have decentralized the functions within the laboratory department. Organizations in the health care industry decentralize the operations, especially in the laboratory because different employees specialize in different areas. Therefore, organizations decentralize the operations to enhance the utilization of the knowledge and expertise of individual employees within the organization (Jeffries and McClean 86).
The decentralization of information based on the specialization of different personnel within the health care organization has affected the operation in the health care industry, especially among employees within the laboratory department. Decentralization is expensive; an organization requires an effective and large number of employees to coordinate the decentralization of information in the laboratory department effectively. The organization will require competent and specialized employees well versed with result analysis, collection, and interpretation in each sub-department. This will require an organization to increase the number of employed personnel within the organization, which is costly, and most organizations strain to employ and maintain a large workforce (Dexter and Traub 938).
There are several organizations in the global industry and economy. Although health care organizations are concerned with the well-being of human health, it is also concerned with making profits. A health care organization increases its returns through the improvement of service delivery, which attracts more clients. The business environment is dynamic, which requires organizations to develop a flexible and competent human resource team, which can respond promptly to the expected changes. Operating cost affects the returns level of an organization (Bielen and Demoulin). Therefore, since health care organizations are also concerned with profit maximization, they must minimize the operating cost. This will enable them to increase their levels of returns. Furthermore, the quality of services offered by respective health care organizations determines customer turnout, which also determines the levels of returns (Dexter, Abouleish and Epstein 1122).
Organizations operate with limited resources. Different organizations compete for the same resources in the global economy, which intensifies competition for resources in the economy. This requires organizations to effectively manage their resources and use them to achieve their set goals and objectives. Although organizations have access to limited resources, they must strive to gain a competitive advantage. An organization gains a competitive advantage in the global market if it acquires, develops, and maintains an effective and competent human resource team. Effective management of limited resources in organizations that have decentralized operations is not easy. This has led to misappropriation and allocation of resources among health care organizations. The laboratory department requires adequate resources to ensure the execution of functions within the department (Gibbs, McGrath, and Russell 13).
Organizations have different goals and objectives. These goals and objectives have priorities, which are not easy to classify in a decentralized operation. A decentralization system of operation ensures that individual departments are concerned with the achievement of the goals and objectives of the respective departments without considering the objectives of other departments within the organization. This leads to confusion in operation in the organization, especially within important departments such as the laboratory (Blake, Carter, and Richardson). The achievements of the prioritized objectives enable an organization to achieve other goals and objectives within the organization. The nature of objectives and goals determines their priorities in an organization (Greenall 9).
Individual departments have projects, which aid in the achievements of the goals and objectives of the organization too. These projects’ implementation depends on their importance to an organization. Implementing projects based on their importance is a challenge for most organizations in the global economy. Successful completion of individual projects leads to the achievement of the overall goals and objectives of an organization (Braaf, Manias, and Riley). Projects’ achievements also depend on the priorities. The prioritized project’s achievements lead to the achievements of other projects, which necessitates the achievements of the overall goals and objectives of the respective organization. Therefore, projects’ implementation in a decentralized system of operation is not easy, which affects the achievements of the goals and objectives of respective organizations within the global economy (Bhalla, Aron, and Donskey 105).
Organizations are set up to prosper and achieve the set goals and objectives. However, an organization has the possibility of failing or succeeding. The nature of the risks of individual projects within an organization determines whether an organization fails or succeeds in the global economy. Furthermore, how respective organizations handle risks is also important because it determines the failure or success of an organization in the end (Butler, Boxer, and Sutherland-Fraser). Organizations managing multiple projects require an effective human resource team, which evaluates and reviews risks associated with individual projects within a portfolio. Effective management of risks ensures that an organization achieves its goals and objectives within the stated or stipulated time or deadline (Dante, Gawande, and Sara). Evaluation of risks in a decentralized system of operation is not easy. This has led to the collapse and failure of several organizations in the global economy. The decentralization system does not enable an organization to effectively assess risks and address them accordingly. Furthermore, the decentralized system of operation does not enable an organization to share the risks that are associated with individual projects towards the achievements of the overall goals and objectives of the organization (Burnes 56).
Most organizations in the health care industry adopt the decentralization system of operation. However, this system is not appropriate for use in laboratory departments. The laboratory department is a major department in health care organizations. It requires an effective and competent human resource team (Christian). Furthermore, the laboratory department requires effective and appropriate strategies. The strategies adopted for use in the laboratory department should ensure that an organization achieves its goals and objectives within the stated deadline or period. The decentralization of information in the laboratory in most health care organizations has led to the failure of the collapse of several health care organizations (Calms and Shusterich). The decentralization of information hinders increased efficiency among health care organizations. This has also affected the returns levels, implementation of quality programs, and initiation of new and effective projects within health care organizations. Furthermore, effective management of risks within health care organizations has not been easy due to the decentralization system of operations (Brooks and Brown 345).
The laboratory department should function effectively. It should aid in the achievements of the goals and objectives of an organization is one of the major departments within health care organizations (Boushy and Dubinsky). However, this is not possible in case a health care organization adopts the decentralization system of operation. The decentralization system hinders increased efficiency in operation among health care organizations. An organization requires effective strategies to enhance efficiency and achieve its goals and objectives within the stated deadline or period. Therefore, health care organizations require a centralized system of operation to enhance efficiency, develop and implement quality programs, improve quality of services and increase returns levels among others (Cummings and Worley 112).
An organization in the health care industry requires improving the quality of services it provides to clients. Increase efficiency in operation by providing clients with their medical reports and results upon inquiry. Increase the analysis and interpretation of results in the laboratory department. This is a challenging task since organizations must develop effective strategies to achieve their goals and objectives (Gibbs, McGrath, and Russell). However, most organizations in the health care industry adopt the decentralization system of operation. This has affected the quality of services provided by organizations in the health care industry. The decentralized system of operation is not an effective system to use in the operation and management of health care organizations considering the nature of the information handled by health care organizations (Jeffries and McClean). Furthermore, the decentralization system does not allow an organization in the health care industry to improve the quality of services as desired. An organization should adopt a centralized system of operation in the health care industry to improve the quality of services offered by the laboratory department, develop and initiate quality programs and increase the levels of returns (Dante, Gawande and Sara 108).
Adoption of the centralized system of operation in the health care organization that intends to improve service delivery in the organization will lead to the introduction of change. Introducing change in an organization is challenging. Employees may accept or resist the introduction of change within an organization (Armstrong and Nicoll). However, an organization must prepare its employees for change before introduction. The change affects employees directly or indirectly. The top management develops changes but employees implement the respective changes within an organization. Change introduction affects the operation of employees directly or directly because it changes the ways of operation and ways of carrying out tasks in an organization. Therefore, the choice of an appropriate model and change process is essential in the successful introduction of centralization of information in the laboratory within the organization (Cox 102).
Change process
The introduction of change in an organization is a challenge to most organizations in the global economy. Change leads to the adoption of new ways of conducting operations within an organization. The nature of change introduced in an organization determines the degree of resistance from employees. There are certain changes within an organization that may lead to moderately high resistance, moderately low resistance, high resistance, and low resistance (Blake, Carter, and Richardson). The development of effective strategies to contain resistance in the event of change introduction is essential towards the successful introduction and implementation of change within an organization. Employees must be educated on the intended change to avoid resistance. Resistance by employees to the introduction of change affects the successful implementation of change within an organization. Organizations must develop strategies that enable effective and smooth implementation of change within an organization (Igor 25).
There are several change models and strategies, which aids in the successful introduction of change within an organization. Choice of a model or strategy depends on the organizational needs and the nature of change that an organization intends to initiate. These models and strategies aid in the successful implementation and initiation of change within an organization (Calms and Shusterich). Although these strategies aid in the successful implementation and initiation of the change process within an organization, they are not perfect, which has led to the development of several change models and strategies to address the changing and dynamic needs of organizations in the global economy. Change introduction by organizations aims at increasing efficiency in operation and increase in the returns levels (HSE).
The health care organization intends to introduce change in the organization to centralize the laboratory information. The laboratory is one of the major departments within a health care organization. The laboratory is responsible for several purposes within the health care organization (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time). Furthermore, the laboratory conducts diverse functions and assists other departments within the organization to achieve its goals and objectives. Ineffectiveness in the laboratory department affects the operation and function of other departments within a health care organization. The organization intends to introduce change in the laboratory because an effective laboratory section aids in the increased efficiency and returns levels of an organization. The organization aims to centralize information in the laboratory. This is a strategy, which assists in increasing efficiency in the organization (Dexter, Abouleish, and Epstein). However, the organization requires the development and implementation of an effective model to aid in the achievement of the strategy successfully. Although there are several models that aid in the introduction of change within organizations, the best model to enable the organization to centralize information in the laboratory is the Health Service Executive model. This model will enable the organization to respond to its needs, address resistance from employees and achieve its goals and objectives within the stated deadline or period (NPSA).
Health Service Executive model
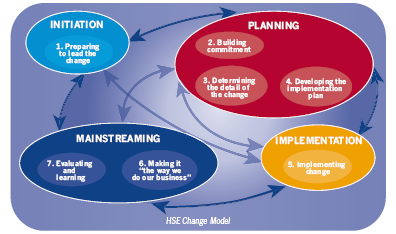
Organizations use several change models to aid in the successful introduction of change within respective organizations. Choice of a model to use depends on the nature of the change, industry of operation, and expected results by the respective organization. Health care organization requires different models considering the nature of their operation and area of specialization. The models applied by health organizations aim at enhancing the provision of quality services among organizations (Barlow). Although there are several models that health care organizations use to aid in the successful introduction of change, this organization requires the effective and appropriate development and implementation of the Health Service Executive model. The Health Service Executive model’s initiation and implementation adopt a stage or phase implementation (HSE). There are four phases or stages that the health service executive model undergoes before successful implementation of change within an organization. The four stages of the health service executive model are planning, initiation, implementation, and mainstreaming. The organization will require an effective and competent management team to develop and implement the health service executive model in the organization. This will enable the organization to centralize the information in the laboratory department and increase efficiency in operation (Odell 1).
Phases or stages of Health Service Executive model
Initiation
This is a stage where the organization will identify the area that it needs to introduce change within the organization. The organization has adopted the decentralization system of operation in the organization. This has led to the decentralization of information in the laboratory department too. Decentralization of operation within the laboratory department affects the achievements of the goals and objectives of the organization, returns levels, development, and implementation of quality services within the organization (Michel, Quenon, and De Sarasqueta). However, the organization intends to increase efficiency in the organization, improve the quality of services offered and increase returns levels in the organization. The organization requires to introduce a strategy that will enable it to centralize the laboratory information. Therefore, the organization prepares to lead the change to successfully introduce the centralization of laboratory information in the organization (Milligan 99).
Preparing to lead the change
Driving need for change in the organization
The organization intends to break away from the decentralization of laboratory information. The decentralization system of operation within the organization has affected the efficient operation within the organization. Generally, the decentralization system of management and operation is expensive and difficult to manage. This has led to decreased efficiency in operation for the past years. Laboratory serves all departments within the organization (McIntosh, Dexter, and Epstein). Basically, the laboratory collects, analyzes, and interprets medical data and information of all clients within the organization. It is also one of the major departments within the organization. Decentralization of operation affects the efficiency of the operation within the department. The organization has attempted severally to improve the quality of services it offers but in vain. This is due to the decentralized system of operations. Furthermore, the company has not increased its return levels as expected over the years. Returns levels of an organization increase if the risk management operates effectively (Michel, Quenon, and De Sarasqueta 203).
Analysis and management of risks within an organization in a decentralized system of operation fail several organizations. Risks management requires a centralized system of operation to enable an organization to review the risks and engage in risk-sharing, which enables organizations to balance risks associated with individual projects within the organization. The decentralized system of management has hindered the organization from analyzing the risks and sharing them evenly to aid in the achievement of the goals and objectives of the company (Park and Dickerson). Therefore, the decentralized system of operation used by the organization in the past has affected the ways of operation and hindered the company from increasing efficiency. This necessitates the need for change. The organization requires a centralized system of operation, especially in the laboratory department to increase efficiency in operation (USCG).
Clarifying roles of leadership and identifying key stakeholders and influencers
The organization requires an effective and competent management team to implement the proposed change successfully. Although management is an important function in an organization, it requires effective leadership too (Bhalla, Aron, and Donskey). Through effective leadership within the organization, implementation of change in the organization will materialize within the stated or stipulated time or deadline. It is through leadership that the organization will guide its employees through the change process geared towards increasing efficiency, returns level, and improving service delivery within the organization (Waring and Harrison 3).
The organization offers medical health services to clients who require or seek the services of the organization. The stakeholders include the patients and employees of the company alongside the shareholders. It is the duty of the shareholders to ensure that the employees access the required resources for the execution of the functions within the organization towards the achievements of the goals and objectives of the company (Bhalla, Aron, and Donskey). On the other hand, employees within the organization develop and implement strategies aimed at increasing efficiency and enabling the company to achieve its goals and objectives within the stated deadline. Therefore, the employees must develop achievable and workable strategies and objectives. Moreover, the shareholders ensure availability of resources for the execution and implementation of strategies and objectives of the company (Weiner and Lewis 408).
Employees within the organization consist of the management team and other general staff members. It is the duty of the top management to develop achievable goals and objectives for the company. Furthermore, it is the duty of the top management to develop strategies, which aids in the achievement of the goals and objectives of the company (Becker and Douglas). On the other hand, the employees implement the strategies developed by the top management in achieving the goals and objectives of the company (Braaf, Manias, and Riley). However, the top management requires the input of the employees during the development of strategies, goals, and objectives of the company. The employees understand the organization better than the top management and the shareholders because they engage in the daily activities of the company (Wiegmann, ElBardissi, and Parker 706).
Clients of the organization play an important role in the development and increased efficiency in operations. Organizations rely on the clients’ feedback to improve the quality of services, which assists an organization to increase returns level. Clients provide feedback to the company through available channels within the company. The communication channels assist organizations to increase efficiency in operation and improve the quality of their services. An organization determines the efficiency of an adopted strategy through feedback offered by clients of the respective organization. Clients appreciate the services offered by an organization by recommending others to seek services of the respective organization (Butler, Boxer, and Sutherland-Fraser). Furthermore, the feedback on improvements of services of an organization originates from the clients’ feedback too. Therefore, it is the duty of the clients and customers to affect the changes made on the quality of services offered by an organization through feedbacking (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time). Furthermore, the employees and management also influence the changes in the operation of an organization. Additionally, the employees and management require the shareholders’ support to obtain the necessary resources required for the implementation of respective strategies developed by an organization (WHO 63).
Considering the situation of the organization, the top management develops the strategy of centralizing the laboratory information after consulting the employees. The top management develops the strategy based on the employees’ recommendations. Employees engage in the daily activities of the organization and understand strategies that the organization requires to increase efficiency. Although it is the duty of the top management to develop strategies and objectives, they consult the employees too (Bhalla, Aron, and Donskey). The management reviews the needs of the organization based on the feedback provided by clients of the organization. It is through the feedback provided by the clients that the organization realized the need to centralize the laboratory information to enhance efficiency in operation and improve the quality of services offered to the expectations of the clients. This will also assist the company increase their levels of returns and achieving their goals and objectives within the stated or stipulated deadline or periods. Therefore, the feedback offered by the clients and customers affects the changes and operation of the organization (Blake, Carter, and Richardson). Although the feedback enabled the organization to identify the need to centralize the laboratory information and increase efficiency through improved service delivery, it also required the intervention and input of both the management and employees of the organization. Additionally, the shareholders also play an important role by ensuring that the required resources for the implementation of the strategy of centralizing the laboratory information are availed to the company as specific within the stated deadline to enable smooth implementation (WHO, More than Words: a conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety 49).
Assessing readiness and capacity for change
The organization must prepare adequately before initiating the change. Changes require adequate readiness and preparedness due to uncertainties involved in the change process. Furthermore, an organization must assess the change capacity to prepare adequately. The organization expects to centralize the laboratory information to increase efficiency and improve services offered to the clients. Centralization of laboratory information is an uphill task that requires adequate preparation considering the nature and capacity of information contained in laboratories. Centralization of resources may lead to the loss of employment by some employees within the organization (Dexter, Abouleish, and Epstein). Furthermore, it may lead to the restructuring of the positions within the organization to suit the new system adopted. Restructuring of organizations requires specialists in job design (Bhalla, Aron, and Donskey). Therefore, the company may face resistance from employees because of the uncertainty of whom to lose his or her job in the process of centralizing information in the laboratory section. The proposed change will force the organization to combine certain duties and functions of some employees, which the company has to prepare the respective employees psychologically to share respective duties for the good of the company. Furthermore, the company will require effective coordination of the functions of the organization to ensure achievement of the goals and objectives of the company (WHO, Improving health quality provision 28).
The functions in the laboratory section are decentralized, which has not enabled the company to increase efficiency. Centralizing the functions will enable the company to centralize the information within the department too (Cummings and Worley). Centralization of information in the laboratory will require effective coordination of sections and sub-departments that handle laboratory information. This will enable the company to determine the capacity for change and readiness to implement the proposed change of centralizing laboratory information. Therefore, considering the factors within the organization, generally, the organization is ready to initiate and implement change through centralization of the laboratory information to increase efficiency in operation and quality of services offered to customers and clients (Barlow 398).
Attending to organizational politics
Individual organizations have politics that play an important role in the introduction of change. Moreover, organizational politics play an important role in the development and adoption of strategies within an organization. The politics may enable an organization to develop and implement an effective strategy, reject an ineffective strategy or reject an effective strategy that could assist the organization to increase efficiency in operation and increase returns levels (WHO, WHO patient safety Curriculum Guide for Medical Schools). Generally, the politics of the organization led to the adoption of a decentralized system of operation, which has affected the quality operation of the organization for the past years. Therefore, convincing the key players in organizational politics is important in the introduction of the proposed change. The benefits of the proposed change over the current system’s discussion and extensive outline to the shareholders and top management team of the organization are essential because they play an important role in the politics of the organization. Their approval of the proposed change is important because it determines whether the organization adopts and implements the change or rejects the proposed change (Becker and Douglas 135).
Opportunities for change and impact of change
The organization has developed a need to change by centralizing the laboratory information. This will enable the company to improve the quality of services it offers to customers and clients. The organization requires improving the quality of services it offers to clients and increasing their returns levels. The opportunity that the organization has to improve the quality of its services is centralizing the laboratory information. Centralization of laboratory information will enable the company to improve service quality as it desires and increase profit levels too (Blake, Carter, and Richardson 269).
Agreeing to the initial resource requirements and an outline of the initial business case for change
The organization requires centralizing laboratory information. The company requires a competent and specialized human resource team, which may respond and analyze the proposed change effectively. Therefore, for the organization to implement the change effectively, it requires to employ a competent and specialized human resource team, which may respond to the proposed change (Bielen and Demoulin 182). After assessing the required resources for the successful introduction of the change, I had to assess and accept the requirements to enable implementation of the proposed change.
Planning
Building commitment
This is an important stage in the planning process of the Health Service executive model. Preparing and establishing commitment among employees and relevant parties is important in ensuring smooth and successful implementation. There are several stages or process that requires adequate attention and address to ensure that commitment building among influencers in the organization succeeds. This strategy involves building a shared vision, communicating business and vision case for the respective change, increasing the readiness and capacity for change, and demonstrating that change is underway.
Building a shared vision
As a consultant contracted to assist the organization to centralize laboratory information, I had a vision of improving the quality of services offered by the company and assisting the company increase their profit levels through increased efficiency and improved service delivery. However, this vision may affect the operation of some employees within the organization because they are used to the decentralized system of operation (WHO, More than Words: conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety). Therefore, I have to educate the employees on the importance of the centralized system of operation, especially in the laboratory being a main department in the organization that may enhance efficiency and improve quality of service delivery. The employees must share in my vision for the proposed change to succeed in the organization and the goals and objectives of centralizing laboratory information achieved within the stated deadline (Wiegmann, ElBardissi, and Parker).
Achieving the goals and objectives of an organization is challenging in case employees and consultants do not share the same vision. This results in divided loyalty, which hurts the performance of most organizations in the global economy. Communicating to the employees the need and importance of centralizing the laboratory operation was important and the first priority towards centralizing laboratory information in the company. This enabled creation and building of a shared vision of creating an organization with a centralized laboratory operation (Becker and Douglas).
Communicating vision and business case for change
Developing and establishing a vision in a change process is not the most important element. However, the vision must prevail in the entire organization for achievement. I had to communicate to the laboratory technicians, assistants, and doctors in charge on the vision and business relevance of the proposed change to ensure its adoption as a medical strategy towards improving quality of services and business strategy used in increasing returns within the organization (Jeffries and McClean). Although the organization offers health care services, and it is concerned with improving quality health care services, it is also concerned with increasing their profit levels being a business corporation. Sections such as microscopic analysis center required centralization because they serve the same purpose of analyzing and evaluating results that require the use of the microscope in interpretation and analysis (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time). Moreover, I had to communicate to the employees within the organization the importance of centralizing the information. Centralizing laboratory information increases the safety of patients too (WHO, WHO patient safety Curriculum Guide for Medical Schools).
Increasing readiness and capacity for change
Change is a process and not an event. It requires adequate preparation and effective strategies to aid in the successful completion of the process. Increasing the readiness of the employees of the organization for the proposed change was a priority. Change introduction in the organization may affect the operations of employees directly or indirectly because it affects the nature of operations. Preparing employees for change is important towards ensuring successful completion and implementation of change within an organization. I had to re-educate employees on the expectations of centralizing laboratory information, the sub departments that required harmonization and the required skills for the centralized system of operation (WHO, More than Words: conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety).
Furthermore, I had to recommend increase in the number of employees within the department after centralization to enhance efficiency in service delivery. A centralized system requires adequate capacity of staff to respond to inquiries from clients and customers promptly. The customer service staff on the laboratory section required increased capacity to aid in quick information access upon inquiry by customers within the organization (McIntosh, Dexter and Epstein). Moreover, I had to constitute a change management committee within the organization to assist in preparing the employees for the change process because employees within the organization know the nature of employees within the company. This assisted in preparing the employees adequately for the proposed change (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time).
Demonstrating that change is underway
Introducing change in the organization is challenging because it is bound to face resistance but the nature of the expected resistance was controllable because employees were aware of a centralized system of operation although the organization had not implemented it in the past. Systematically doing away with related departments and integrating relevant departments was an action that demonstrated that centralization of the laboratory information was underway. There were certain departments that served as laboratory information centers for individual sections and departments within the organization (McIntosh, Dexter, and Epstein). However, all information collected by personnel from the laboratory department requires centralized storage to enable easy access to information from the laboratory. Accessing decentralized laboratory information is not easy, and has led to difficulty in customer service and quality delivery to customers, which has affected the operations of the organization over the past years (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time).
Determining the detail of the change
I had to determine the details of the change to ensure successful initiation and implementation. Generally, assessment of the current situation in the organization against the future vision for changes was important. Secondly, I reported the analysis to the key stakeholders of the organization. Finally, I described what the company needed to change to increase efficiency in operation and possibly increase return levels (Bhalla, Aron, and Donskey).
Assessment of the current situation against the future vision for change
The organization operates under a decentralized system of operation. This has contributed to the decentralization of laboratory information. However, the laboratory should operate as a unit hence information relevant to the department store in a central place for easy access. The decentralized system of operation has hindered easy access of information by relevant parties and personnel within the organization. This has also affected the possibility of the company to increase returns and improve the quality of services within the organization. Moreover, it has also affected the safety of patients’ information (Dante, Gawande, and Sara). On the contrary, the centralized system of operation proposed aims at centralizing laboratory information in the company. Secondly, the centralized system will enable the company to give customers and clients easy access to their medical information within the organization. This will enable the organization to increase efficiency and improve the quality of service delivery. Moreover, the centralized system will enable the organization to increase returns levels (WHO, WHO patient safety Curriculum Guide for Medical Schools). Therefore, the new proposed change of centralizing laboratory information will enable the organization to improve the quality of services, increase return levels and increase efficiency in operation.
Feedback this analysis to key stakeholders
The organization has stakeholders concerned with increased efficiency and return levels. However, the organization achieves this through improved service delivery because customers are attracted to quality services, which determines the levels of profits the organization, makes in the long run. I had to discuss with the stakeholders the importance and advantages of centralizing the laboratory information. The organization has operated under a decentralized system of operation, which has affected the profit levels and quality of service provision (Butler, Boxer, and Sutherland-Fraser). Furthermore, this has not enabled the organization to give patients easy access to their medical information. However, the centralized system of operation, which will lead to the centralization of laboratory information, will enable the organization to give patients easy access to their medical information, increase efficiency in operation and improve the quality of services offered. Stakeholders are concerned with the survival of the organization and profit levels, especially the shareholders. Therefore, I had to discuss and outline to the shareholders the impacts and advantages of centralizing laboratory information to the survival of the organization and profits levels too. The shareholders are motivated to invest more in an organization in the event of high profits and return growth speculation and forecast and guaranteed growth, which will lead to increased profit levels and competitive advantage gaining (WHO, WHO patient safety Curriculum Guide for Medical Schools).
Describing what needs to change
The organization is required to centralize laboratory information. Centralization of the laboratory information will lead to changing several aspects and structures in the organization. The structure of the organization will need to change to accommodate the centralization of the laboratory information. Centralization of laboratory information will require a centralized system of operation for successful and full implementation of the proposed change in the organization (Becker and Douglas). The centralization of the laboratory information also expects harmonization of certain duties and functions within the organization such as the collection and analysis of patients’ information. These duties and functions require central location operation to enable centralization of laboratory information. Moreover, a central storage requires set up to enable the organization to direct laboratory information in a central place within the organization. Additionally, laboratory information handling will be directed to a specific point or department to enable easy access and storage. Filling system in the organization will also be changed to enable easy storage and access of information within the organization (WHO, More than Words: conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety).
Developing the implementation plan
Planning is an important aspect that enables organizations to achieve their goals and objectives within the stated deadline. Effective planning enables an organization to increase efficiency. Health care organizations require effective planning to improve the quality of services. Development of an implementation plan is the final stage or phase in the planning process in the Health Service Executive model. There are several functions that I had to conduct to enable the successful initiation and implementation of the proposed change. Basically, I had to design the detail of the future state, assess the impact of the detailed design, outline and agree the plan for implementation and complete the detailed implementation of the proposed change.
Designing a detail of the future state
Centralizing laboratory information will change the structure and operation of the organization in future. The organization currently uses a decentralized system of operation while centralization of laboratory information will lead to the adoption of a centralized system, which will change the structure of the company in several ways. In future, collection, analysis and storage of the laboratory data will be centralized. This will require individual patients within the organization to search for their medical records from a central point irrespective of the medical department responding to their needs within the organization. Patients will also have to register an inquiry to access their medical information in person to avoid access by unauthorized persons to the information of other patients within the organization. This process is developed to aid in patients safety and improve service delivery to individual patients within the organization (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time).
Assessing the impact of the detailed design
Centralization of laboratory information is important for the organization because it will enable the management team to achieve the goals and objectives of the company within the stated deadline. Generally, the centralized information system will enable the organization to improve the quality of services to patients because information access in the organization will be enhanced. Furthermore, efficiency will be increased in the organization because centralizing laboratory information will enable the management to easily and efficiently supervise and coordinate operations within the department and the organization (USCG). Safety of patients will be increased through centralization of laboratory information. The laboratory stores important and confidential report concerning the health status of patients, which require confidential storage. The centralized system will enable the organization to protect patients’ medical information from unauthorized access because they will be accessed by the patients and employees responsible for collection, analysis and interpretation of laboratory data (WHO, More than Words: conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety).
Outlining and agreeing the plan for implementation
The detailed plan will aid in the implementation of the proposal successfully in the organization. As a consultant, I required the support of the employees within the organization and stakeholders and shareholders. Moreover, the support of the management team was crucial in ensuring that the change is systematically introduced in the organization through the supervision channels available in the organization. There are processes that I require to develop before committing the plan to full implementation. The plan will serve as a road map to the implementation of the project. Generally, the management required training on restructuring of the organization and building of a new facilities to accommodate a centralized laboratory within the organization (Calms and Shusterich).
Completing the detailed implementation
Spacious structures’ constructions to aid in the centralization of the information within the laboratory initiation completed. Thereafter, educating the existing employees on how a centralized system operates, and aiding them with the required knowledge to implement a centralized system of organization. The human resource team required to assess the human resource needs of the organization and make relevant recommendations. Moreover, the human resource department to assist in the restructuring of the organization by creating new positions and integrating existing positions with conflicting duties and roles within the organization. This will enable the full implementation and successful completion of the proposed change (Michel, Quenon and De Sarasqueta). Moreover, the cooperation of the shareholders and top management is required because they are responsible for approval and rejection of projects and strategies within the organization. The shareholders provide resources, while the management assists in the development and adoption of strategies that can enable the organization to increase efficiency, returns and improve quality of services offered (Gibbs, McGrath and Russell).
Implementation
Implementation of the change
Change implementation in an organization requires an effective strategy and planning. After effectively planning for the process, a change is easily initiated and implemented because planning takes uncertainties into consideration hence enabling an organization to handle them effectively. This is the practical stage or phase of the Health Service Executive model because it involves the realization of the plans of the organization. This stage involves the implementation of the proposed change and sustains the respective momentum for the benefit of the organization (NPSA).
Implementing the change
Ensuring the centralization of laboratory information is the main objective of the proposed change. Therefore, ensuring that laboratory information is centralized reflects the full implementation of the change. I had to coordinate the collection and attainment of resources required in the process, coordinate the process with the top management, and mobilize full support of the process. The collection, analysis, and interpretation of data will be located in one location, which means laboratory information within the organization will be handled by employees from the same department (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time). This will increase efficiency in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data collected. The laboratory individuals will be assigned to all departments within the organization to enable easy access and collection of data that requires laboratory services. All information collected and analyzed in the laboratory will be stored in a central place using a centralized filling system to enable easy access and retrieving of data within the organization (WHO, More than Words: a conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety).
Sustaining momentum
Implementing the proposed change may be easy but maintain the implementation process is challenging because employees may resist the change. As a consultant, I will ensure that the momentum is sustained by introducing strategies such as frequent review and evaluation of the implementation process. This will enable me to make relevant changes and recommend required resources for the full implementation of the change in the organization. Furthermore, I will constitute another operational committee to assist the planning committee in the implementation process. This is due to the increased functions and nature of the change being implemented. The change will lead to changes in the structure and duties and roles of employees, which requires the input of existing employees too. This will enable the organization to sustain the initiated change process (American College of Physicians). However, sustaining the change to full implementation will be challenging. Apart from the human resources, the change requires financial resources for the achievements of its goals and objectives. The financial resources provided by the stakeholders will be used in increasing the number of human resources used in the implementation of the change. Secondly, it will be used in the expansion of department to host the centralized laboratory. Moreover, the financial resources will be used in developing and establishing a reliable filling system to sustain the change to full implementation (O’Neil and Dexter).
Mainstreaming
This is a process of maintaining and fully sustaining a change for future use. Mainstreaming also involves working towards adopting an implemented change as the strategy of an organization for future use and incorporating it fully into the system and structure of the organization. After centralizing laboratory information, I will ensure that the organization adopts a centralized system of operation to ensure the change contributes to the achievements of the goals and objectives of the company, and does not collapse (Barrs).
Making it the way we do our business
Making the strategy way of business is a step towards maintaining the change in the organization. There are several strategies that will ensure that centralization of laboratory information is adopted in the organization and used as a business method within the organization. To make centralization of laboratory information a strategy within the organization fully, its achievements and success will require acknowledgment, integration of change will require support, and ensuring decision making within the organization supports the change.
Acknowledging achievement and success
Centralization of laboratory in the organization will enable the company to improve the quality of services, increase efficiency and levels of returns. This will be acknowledged to ensure that employees within the organization value the change and work towards protecting, and ensuring it succeeds in the organization. The best way to acknowledge the achievements and success of the change is attributing the contributions of the strategy to the organization after introduction and implementation. The organization through the management will ensure that changes such as improved service quality and increased efficiency associated with centralization are acknowledged during annual meetings and financial reporting among other events of the organization (Park and Dickerson).
Supporting integration of the change
The change requires support during integration with the system of the company. The change may require changes from time to time due to the dynamic nature of the business environment. It is the duty of the management team to ensure that required resources that can support the operation of the change are injected to ensure smooth operation. Moreover, after implementation, it is the duty of the top management to take over the change and ensure it succeeds (Berwick).
Ensuring the decision making processes support the change
Initially, the organization was using a decentralized system of operation. However, the centralization of laboratory information cannot function appropriately under a decentralized decision-making process. Therefore, the organization will have to adopt a centralized system of operation to enable the centralization of the decision-making process. This will ensure that the decisions made within the organization serve the interest of the change and contribute to increased efficiency and performance. Therefore, I will ensure that the organization adopts a centralized system of operation in the entire management and operations of the organization to support the centralized laboratory information introduced in the organization (Boushy and Dubinsky).
Evaluating and learning
This is the last stage in introducing change in an organization using the Health Service Executive model. This stage ensures that the change assists the organization to achieve its set goals and objectives within the stated deadline without making any changes. There are several stages involved in this stage to ensure the introduced change is maintained in the organization. Moreover, the process ensures that the management introduces and adopts better strategies in the future that support the change. They include building a system to refine and continuously improve the implemented change, learning from the change process, and establishing best practices for change (Armstrong and Nicoll).
Building a system to refine and continuously improve
A system within the organization will be developed to ensure it refines and improves the change. The best system for this purpose will be simulation and modeling of an effective Project Portfolio Management System because the organization will be handling several projects within one department. This will ensure that the goals and objectives of the company are achieved (Braaf, Manias, and Riley).
Learning from the change process and establishing best practices for change
Centralization of laboratory information leads to the improvement of service delivery in the organization. Furthermore, it assists the organization to increase efficiency in operation and returns level. This is important because the organization should learn the importance and advantages of centralizing operations through this strategy. This should enable the organization to adopt a centralized system of operation and abandon the decentralized system to reap the benefits of centralizing operation (Dante, Gawande, and Sara).
Reviewing the temporary change support structures, systems, and roles
Reviewing a system is the best method to evaluate and monitor a respective system. This will ensure that an implemented or initiated change concurs with the strategies and models adopted in the respective organization. I will ensure that the organization frequently reviews its systems, roles, and structures to ensure it supports the introduced change (WHO, WHO patient safety Curriculum Guide for Medical Schools). Generally, decision-making roles require centralization to ensure it supports the centralization of laboratory information, furthermore, the organization requires to adopt a centralized system of operation to support the change. Moreover, the structure of the organization should be centralized to ensure that operations within the organization support a centralized system of operation because centralization of laboratory information requires a centralized system to operate efficiently (WHO, More than Words: a conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety).
Evaluation
The change should enable the organization to improve quality, increase efficiency in operation and profit levels. The change process will require large amounts of financial input to ensure full implementation. The change requires changes in several structures and systems within the organization that requires financial input. Establishing the filling system in a centralized system of operation requires financial support from the organization. Moreover, training of employees and constructing a spacious facility to host the centralized laboratory unit will also require financial input within the organization (Abdel-Galil).
Summary
The change process enabled the organization to centralize laboratory information and increase efficiency in operation. Moreover, evaluation tools such as focus group discussions were used to ensure the change is sustained within the organization.
Discussion and conclusion
Organizations require achieving their set goals and objectives to consider themselves successful. There are several organizations in different industries globally, which has led to increased and intense competition among companies in the global market and economy. Furthermore, there are limited resources that companies compete to acquire. Although resources in the global economy are limited, the objectives and goals of organizations are unlimited. Therefore, organizations must use limited resources to achieve their unlimited goals and objectives within the specified time or deadline. Organizations require developing achievable goals and objectives (WHO, More tha an Words: conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety). Furthermore, goals and objectives of an organization require the consideration of the clients’ feedbacks and the employees’ response because they engage in the daily activities of the organization. The organization requires centralizing the laboratory information to increased efficiency in operation. Decentralized system of operation is disadvantageous and may not enable an organization to respond promptly to the frequent changes in the business environment (Berwick 35).
The business environment is dynamic, which leads to frequent changes. Furthermore, organizations have no direct influence over the external factors of business environment, but they affect the operations of all organizations in the global economy. Organizations require effective strategies and competent human resource team to respond to the changes promptly. Response to the changes in the business environment determines the success and levels of returns of respective organizations in the global economy (Bhalla, Aron and Donskey). Although there are several strategies and models that organizations may use to increase efficiency in operation. It requires an effective and competent human resource team, especially the top management to decide on the most appropriate strategy based on the organizational needs and requirements. The organization expects to increase efficiency in operation and improve the quality of services it offers through the centralization of laboratory information.
Centralization of laboratory information is important because it is one of the major departments and sections within a health care organization (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time). Centralization is an important strategy that the organization may apply or implement to increase efficiency in operation, increase returns level and improve the quality of services offered towards the achievements of the goals and objectives of the respective company. The setting of goals and objectives within an organization is an easy task, but working towards the achievements of the set goals and objectives is an uphill task, which requires an effective strategy and competent human resource team (WHO, More than Words: a conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety). The organization has worked with a decentralized system of operation for a long time without any recommended changes from the employees. This has affected the performance of the company for the past years and hindered the company from achieving its goals and objectives within the stated deadline or period (Braly 14).
Centralization of the laboratory information will assist the company increase efficiency in operation, improving the quality of services offered, and achieving set goals and objectives within the stated deadline or period. Centralization of the laboratory services will enable the company to assess the progress of individual projects regularly, which increases efficiency in handling projects. Furthermore, it will enable the company to evaluate the risks associated with individual projects hence share the risks, which will enable the company to achieve the set goals and objectives within the stated deadline or period (Boushy and Dubinsky 408).
Recommendations
The organization intends to increase efficiency in operation, improve the quality of services it offers and achieve its set goals and objectives within the stated deadline or period. There are several strategies that the organization can use to increase efficiency. Moreover, there are models that the organization may apply to enable it to achieve its developed strategies within stated deadlines. The organization intends to centralize the laboratory information. The laboratory is a major department in a health care organization. The organization should develop an effective strategy that enables effective centralization of the laboratory information (WHO, More than Words: a conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety). The laboratory contains important information about individual clients and customers of an organization providing health care services. Although there are several strategies that the company may use to centralize the information, the most appropriate strategy or model is the development and implementation of an effective and appropriate Project Portfolio Management System (Kotter 65).
Project Portfolio Management System
Project Portfolio Management System is one of the most appropriate strategies that organizations may use to centralize operations and increase efficiency, achieve set goals and objectives while increasing the levels of returns. Project Portfolio Management System will enable the company to centralize laboratory information effectively because it encourages centralization of operations (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time). A laboratory assists several departments and sections within a health care organization to achieve its goals and objectives. Achievements of the goals and objectives require an effective and competent human resource team. Furthermore, it requires the development of effective strategies, which aids in the achievement of the most important goals and objectives within the organization (Macario 28).
A laboratory is the core of operations of health care organizations because it contains all health records of individual clients and customers of respective organizations. Therefore, a laboratory in a health care organization means everything to the respective organization because, without a laboratory, health care organizations may not operate effectively and aid in increased operations of health care organizations. Laboratories assess the data of all clients in a health care organization (WHO, WHO patient safety Curriculum Guide for Medical Schools). Moreover, all sections and employees within a health care organization utilize the laboratory to assess, collect, analyze and interpret data of individual clients within a health care organization. Since the laboratory handles several data from different clients and departments within the organization, it holds the key to the success of any health care organization (Kotter, Winning at change 30).
The laboratory is a health care organization because it is the most important department within the health care industry. It also handles several data, which aims at producing different results based on the information collected (Armstrong and Nicoll). Therefore, it is true to consider a health care organization as a project-based organization managing multiple projects. The inquiries by different clients based on their medical status are projects, which require an appropriate strategy and an effective human resource team to address. Project based organizations managing multiple projects require an effective strategy, which can enable the respective organization to manage the projects and successfully implement them. Furthermore, project based organizations requires to achieve the goals and objectives of individual projects within a portfolio because they contribute to the achievements of the goals and objectives of respective organizations (Kotter, Leading Change, why transformation efforts fail 2).
Effective risk management
Project Portfolio Management System enables organizations to centralize their operations. This enables organizations to regularly review and evaluate the progress of individual projects within a portfolio. Different projects face challenges of successful implementation due to risks. Risks associated with different projects within a portfolio differ. These risks affect the full implementation of individual project and the achievements of the overall goals and objectives of an organization implementing the respective project. Effective evaluation and response to the risks associated with all projects within organizations managing multiple projects is challenging in cases where organizations adopts the decentralized system of operation (Wiegmann, ElBardissi, and Parker). However, Project Portfolio Management System enables an organization to centralize its operations, which enables it to review the risks associated with individual projects within a portfolio. This enables an organization to manage the risks and achieve the goals and objectives of individual projects, which enables the respective organization to achieve the overall goals and objectives of the company (Cummings and Worley). Therefore, the organization should simulate, develop and implement an effective Project Portfolio Management System because it will enable the organization to monitor, review, and manage risks associated with individual projects within the portfolio hence achieving the goals and objectives of individual projects within the stated deadline (McIntosh, Dexter and Epstein 1500).
Appropriate allocation of resources
Allocation of resources among projects within organizations managing multiple projects is a challenge. This has led to the collapse and failure of most projects in project-based organizations managing multiple projects. Different projects require different resources, and in different quantities. A project requires the required resources for full implementation and successful completion. Adequate resource allocation among projects within a portfolio is a challenge to most companies managing multiple projects because several organizations adopt the decentralized system of operation (Armstrong and Nicoll 582). The decentralized system of operation is challenging to implement in project-based organizations managing multiple projects. This system does not enable an organization to concentrate on the progress of individual projects within the organization equally. Generally, the system may lead to the achievement of some projects but not all. Moreover, it might lead to the non-achievement or collapse of important projects that required a surplus supply of resources to implement (O’Neil and Dexter 360).
Allocation of resources among projects within an organizational portfolio requires priority. There are certain projects within an organization that requires the attention of the organization because achievements of its goals and objectives contribute to the achievements of the goals and objectives of other projects within the portfolio. Therefore, such projects require adequate resource supply (Dexter and Traub, How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time). Implementation of Project Portfolio Management System will enable the organization to review and evaluate the performance of all projects within the portfolio equally. This will enable the organization to determine the resources required by individual projects, projects that need changes or amendments, projects that cannot succeed hence dropped, and most important projects of the organization. Misappropriation or allocation of resources among projects within organizations is a challenge that has contributed to the collapse of several projects initiated by organizations (WHO, More than Words: a conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety). Therefore, the adoption of an effective Project Portfolio Management System will enable the organization to closely review and monitor its projects, and allocate resources to each project based on its requirements and importance to the organization and achievements of the overall goals and objectives of the company (Malhorta 86).
Minimize operational costs
Organizations in the global economy operate towards profit maximization. Generally, resources in the global economy are limited, but organizations have unlimited goals and objectives, but must use the limited resources to achieve the unlimited goals and objectives. Financial resources are one of the resources that organizations must manage effectively. The expenditure patterns of organizations in the global economy determine the levels of returns of organizations (American College of Emergency Physicians 1387). Wise-spending organizations maximize profits because they cut down on unnecessary expenditures that may increase the operational cost of the company. Furthermore, all organizations incur the operational cost because financial resources aids in the execution of functions of an organization. Organizations must use financial resources to function properly in the organization. Although effective management and wise spending is important towards returns increment, the level of expenditure determines the levels of returns too (Voigt 19).
Most organizations adopt the decentralized system of operation yet they manage multiple projects. This force such organizations to prepare distinct budgets for individual projects based on the requirements of the projects’ managers and a team of employees. The decentralized system of operation and management is expensive because it does not enable an organization to develop and implement cost-sharing strategy (Barcombe 34). However, Project Portfolio Management System enables an organization to centralize the operations and management of multiple projects within the organization. This will enable the company to share costs evenly among projects within the portfolio (WHO, WHO patient safety Curriculum Guide for Medical Schools). Moreover, it will enable the company to minimize the operational cost and maximize on returns. Therefore, the organization should adopt and implement Project Portfolio Management System because it will enable the organization to centralize the operations and management of the multiple projects within the organization. This will enable the organization to develop and adopt the strategy of cost sharing, which will aid in the minimization of operating cost within the organization, while maximization the returns and profits levels (Watchel and Dexter 220).
Adoption of effective change initiation strategies
Introduction of change within an organization is not easy. Employees in most cases resist change. This requires the management of an organization to develop and adopt effective strategies in the process of implementing change to ensure successful implementation. The strategy that organizations use to respond to resistance from employees in the event of introducing change depends on the nature and degree of resistance (Cosgrove 86). A resistance may be low moderate, high moderate, high or low. These resistances require different strategies to control. Considering the nature of change the organization intends to introduce in the organization, it is likely that the organization may encounter a moderate low resistance from employees (Park and Dickerson 245).
The organization is most likely to face a moderate low resistance because employees have relevant and adequate knowledge on operational system that organizations may use. Moreover, there are certain employees within the organization that have adequate and appropriate information on the centralized system of operation. Although the employees have information on a centralized system of operation, they are most likely to resist its implementation slightly because they are used to the decentralized system of operation and have never worked under a centralized system of operation within the organization (Bartholomew 18). The employees may also resist the change because they are uncertain of the outcome of the change on their positions and employment status. This may cause uncertainty whether the organization will fire them or retain them in the organization but serving under different positions. Moreover, some employees may resist the change because they fear loosing their current position because they feel in a comfort zone (Stanton 16).

Considering the nature of the resistance that the organization may face from employees, the management requires to conduct a research among employees on their views on a centralized system of operation. This will enable the organization to understand the fears of the employees and decide on the best method to use in introducing the change in the organization. Generally, the organization will require re-educating the employees on the centralized system of operation to smoothly initiate and implement the change within the organization (Barrs 20). Although the company may decide that it requires educating the employees on the proposed change, they must collect information from employees to determine the educational needs. This will enable the organization to provide employees with important information about the proposed change hence accept the initiation and implementation of the change without further resistance. Therefore, the organization will require developing a re-education strategy to provide the employees with relevant information on the proposed change to avoid further resistance and pave way for smooth initiation and implementation of the proposed change because it is for the betterment of the organization (Watson 462).
Conclusion
Several organizations adopt the decentralized system of operation, which has affected the operation and development of several companies around the globe. The decentralized system of operation and management does not enable an organization to monitor the operation of all aspects and departments closely. Furthermore, it also affects the response of an organization to matters that require an urgent response. Moreover, a decentralized system of operation is not recommendable for project-based organizations managing multiple projects. Multiple projects require regular and close supervision to enable the respective organization to achieve the goals and objectives of individual projects and subsequently achieve the overall goals and objectives of the organization. Achievements of the goals and objectives of individual projects within an organization lead to the achievements of the goals and objectives of the respective organization.
Reflective Diary
Stage 1: Description of the Event
This reflective diary will cover my experience as a consultant in assisting a health care organization adopts the centralized system of operation and subsequently centralize laboratory information. What I had to do is develop a strategy that the organization could use in centralizing the laboratory information. Moreover, I had to assess and determine the best change management model that a health care organization could use to introduce and implement change successfully. The organization wanted to determine a strategy that could lead to an effective change within the organization. As a consultant, I decided that it had to centralize the laboratory information to change the way of operation. I decided to use the Health Service Executive model to assist the organization introduce the change successfully. On the other hand, the organization decided to centralize its laboratory information. To establish the process of change and implement the proposed change, I had to seek the approval of the top management and the stakeholders of the organization. Moreover, I had to communicate with the management team to assist me in the collection of relevant information from employees to determine the nature of expected resistance. Additionally, I had to communicate with the management team to assist me select committee members to assist me in the initiation, implementation and assessment of the change proposed. I had to conduct and follow up these processes because I was the consultant, and acted as the project leader for the organization.
Stage 2: Feelings
Initiating and implementing this change was challenging. Basically, it was challenging introducing and implementing change that would improve performance of the organization because the organization had undergone losses in the previous years and required an effective strategy to change the trend of increasing losses. I remember feeling nervous the first time I had to meet with the top management of the organization and inform them of the change strategy. I had not worked with such a big organization in the past as the project leader. However, I took this as a challenge because much was expected from me as the leader. Moreover, it was challenging coordinating a large tam of employees and management because the organization had a large number of staff.
When the event started, I doubted if the objective of the project could be achieved within the stated time because it had a strict deadline. Secondly, I expected the employees to resist the change because it is the nature of employees to resist introduction of any change in an organization. I wondered how I could contain the resistance, and enable the organization achieve the objective of the project within the short deadline provided by management. This triggered thoughts on how to summarize the project and incorporate strict supervision to enable achievement of its objective. However, I was surprised by the response of the employees as the resistance was not high, and the cooperation of the management team and the stakeholders was motivating. This made me feel valued and special for the organization. Generally, the response of the organization and its employees made me realize the value of my services as a consultant because they adhered to my instructions.
When the project was summarized, I was surprised that I was able to meet the expectations of the organization, and achieved the objective of the project. Since the objective of the project was achieved, I feel the quality of services of the company will improve and patients will easily access their medical reports.
Stage 3: Evaluation
After introducing the change and centralizing laboratory information in the organization, the quality of services in the company improved because patients could easily access their medical reports upon inquiry. Considering the results, this change improved health care provision to patients and enhanced safety of patients’ health records because they were only accessible to authorized personnel only. The centralized system increased efficiency in operation within the organization. Moreover, the change proved effective because it enabled the organization increase the number of loyal customers due to the improved services. The functions and roles of employees were also simplified.
Stage 4: Analysis
The project faired on well because I received the approval of the management to implement the project. Secondly, the stakeholders were willing and committed the required financial resources towards the implementation of the project. I had to arrange several meetings with the staff and management team, which was not easy but the management made this possible. Although there were difficulties in the process, they were normal challenges but the staff and management cooperated more than I expected, which made the implementation of project easier. Additionally, I was able to address the resistance from the employees through offering education on the proposed change and relying on the information from the management based on the expectations of the employees.
Stage 5: Conclusion
After successful implementation of the project, the operation and management of the organization improved. Decision making process in the organization was enhanced and simplified since the organization adopted a centralized system of operation, the profit levels increased because the organization was able to minimize operational costs. Furthermore, the patients could easily access their health records when needed. Collection, analysis and interpretation of patients’ information within the laboratory department were also simplified and efficiency within the department increased too. The organization easily increased their return levels as desired. Therefore, the successful implementation of the project improved the status of the organization due to the increased efficiency.
Stage 6: Action Plan
Considering the results achieved by the organization, it can be noted that Health service Executive model is an effective strategy of introducing and implementing change within an organization successfully. Moreover, centralization of laboratory information is important in increasing efficiency in operation and quality of service delivery within health care organizations. However, this strategy cannot be applied single handedly to achieve the expected results. It requires incorporation with the Project Portfolio Management System to assist a health care organization enhance better management of the projects within its portfolio.
Works Cited
Abdel-Galil, Kevin. “The WHO surgical safety checklist: are we measurring up?” British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (2010): 397-398. Print.
Armstrong, Denis and Mercy Nicoll. “Consultant’s workload in outpatient clinics.” British Medical Journal (1995): 581-582. Print.
Barcombe, Jerald. “Management in the health care industry.” Nursing Management (2004): 34. Print.
Barlow, George. “Auditing hospital queuing.” Managerial Audit Journal (2002): 397-403. Print.
Barrs, Humphrey. “Change management in project based organizations.” Management and Change (2005): 19-22. Print.
Bartholomew, Jacobs. “Leadership in the Health Care industry.” Medicine and Leadership Practices (2009): 13-19. Print.
Baulcomb, John Steven. “Management of change through focused force field analysis.” Journal of Nursing Management (2003): 275-280. Print.
Becker, Francis and Stephen Douglas. “The ecology of the patient visit: physical attractiveness, waiting times, and perceived quality of care.” Journal of Ambulatory Care Management (2008): 128-141. Print.
Berwick, Densen. “Seeking Systemness.” Healthc Forum (1992): 35. Print.
Bhalla, Aaron, David Collins Aron and Charles J Donskey. “Staphylococcus aureus intestinal colonization is associated with increased frequency of S. aureus on skin of hospitalized patients.” BMC Infectious Diseases (2007): 105. Print.
Bielen, Farouk and Nelson Demoulin. “Waiting time influence on the satisfaction-loyalty relationship in services.” Managing Service Quality (2007): 174-193. Print.
Blake, Jeremy, Mickey Carter and Samuel Richardson. “An analysis of emergency room wait time issues via computer simulation.” INFOR (1996): 263-273. Print.
Boushy, Denis and Ian Dubinsky. “Primary care physician and patient factors that result in patients seeking emergency care in a hospital setting: the patient’s perspective.” The Journal of Emergency Medicine (1999): 405-412. Print.
Braaf, Samuel, Evans Manias and Rodgers Riley. “The role of documents and documentation in communication failure across the perioperative pathway: a literature review.” International Journal of Nursing (2010): 1. Print.
Braly, Danish. “Seek alternatives via simulation software.” Health Management Technology (1995): 13-15. Print.
Brooks, Ian and Rachel B Brown. “The role of the ritualistic ceremonial in removing barriers between subcultures in the National Health Service.” J Adv Nurs (2003): 341-352. Print.
Burnes, Brian. Managing change: A strategic approach to organizational dynamics. Essex, England: Prentice Hall, 2000. Print.
Butler, Michael, Evans Boxer and Stephen Sutherland-Fraser. “The factors that contribute to count and documentation errors in counting.” ACORN Journal (2003): 10-14. Print.
Calms, Seth H and Kelvin M Shusterich. “Operating room management: what goes wrong and how to fix it.” Physician Executives (1992): 11-12. Print.
Christian, Colins Klein. “A prospective study of patient safety in the operating room.” Surgery (2006): 159-173. Print.
Cosgrove, Samuel E. “The relationship between antimicrobial resistance and patient outcomes: mortality, length of hospital stay, and health care costs.” Clin Infect Dis (2006): 82-89. Print.
Cox, Seth. “The structure of employee attitudes to safety: a European example work and stress.” Journal of Leadership in Medical Service (1991): 93-106. Print.
Cummings, Thomas G and Charles G Worley. Organizational development change. Canada: South Western, 2008. Print.
Dante, Maurice F, et al. “Factors associated with effective implementation of a surgical safety checklist.” Journal of the American College of Surgeons (2010): 108. Print.
Dexter, Francis and Rachel Danish Traub. “How to schedule elective surgical cases into specific operating rooms to maximize the efficiency of use of operating room time.” Anesh Analg (2002): 933-942. Print.
Dexter, Francis, et al. “Use of operating room information system data to predict the impact of reducing turnover times on staffing costs.” Anesh Analg (2003): 1119-1126. Print.
Gibbs, Valentine, Maurice McGrath and Thomas Russell. “The prevention of retained foreign bodies after surgery.” Bulleting of American College of Surgeons (2005): 12-14. Print.
Greenall, Paul. “Managerial process: the reflective practitioner.” Leadership in Health Services (2004): 8-11. Print.
HSE. Improving our services- A users’ Guide to managing change in the Health Service Executive. Article Review. Dublin: Health Services Executive, 2008. Print.
Igor, Belyansky T.R. “Poor resident-Attending Intraoperative Communication May compromise Patient Safety.” Journal of Surgical Research (2011): 25. Print.
Jeffries, Valerie D and Gregory P McClean. Pricinciples and practice of Management. London: Cengage Learning, 2010. Print.
Kotter, James. “Change Management; models and strategies: eight steps to transformational change.” Harvard Business Review (1995): 59-67. Print.
“Leading Change, why transformation efforts fail.” Harvard Business Review (1995): 1-3. Print.
“Winning at change.” Leader to Leader (1998): 27-33. Print.
Macario, Annastacia. “Are your operating rooms being run efficiently?” Anesthesiology (2010): 28. Print.
Malhorta, Vincent. “What should anesthesiologists know about operating room management.” Revista medicacane de anestesiologisia (2006): 83-88. Print.
McIntosh, Charles, Farouk Dexter and Raphael Epstein. “The Impact of service-specific staffing case scheduling, turnovers and first case starts on anaesthesia group and operating room productivity: A tutorial using data from an Australian hospital.” International Anaesthesia Research Society (2006): 1499-1516. Print.
Michel, Philis, et al. “Comparison of three methods for estimating rates of adverse events and rates of preventable adverse events in acute care hospitals.” BMJ (2004): 199-328. Print.
Milligan, Joseph F. “Establishing a culture for patient safety – The role of education.” Nurse Education Today (2007): 95-102. Print.
NPSA. Seven steps to patient safety: An overview Guide for staff, second print. 2004. Web.
Odell, Michael. “Human factors and patient safety: Changing roles in critical care.” Australian Critical Care (2011): 1. Print.
O’Neil, Lawrence and Farouk Dexter. “Tactical increase in operating room block time based on financial data and market growth estimates from data envelopment analysis.” Anesh Analg (2007): 355-368. Print.
Park, Kevin Williams and Collins Dickerson. “Can efficient supply management in the operating room save millions?” Current opinion Anaesthesiology (2009): 242-248. Print.
Physicians, American College of Emergency. “Emergency care guidelines.” Annals of Emergency Medicine (1986): 1385-1389. Print.
Stanton, Charles. “Preparing tomorrow’s perioperative staff today.” Leadershipin Medical Service (2010): 12-18. Print.
USCG. Department of Defense Human Factors Analysis and classification System: A mishap investigation and data analysis tool. 2005. Web.
Voigt, Thomas. “Operation’s performance improvement a technology solution.” Surgical Services Management (2000): 15-21. Print.
Waring, James and Steven Harrison. “Safety and complexity: Inter-departmental relationships as a threat to patient safety in the operating department.” Journal of Health Organization and Management (2006): 3. Print.
Watchel, Raymond and Francis Dexter. “Tactical increase in operating room block time for capacity planning should not be based on utilisation.” Anesth Analg (2008): 215-226. Print.
Watson, Denis. “Counting for patient safety.” AORN (2006): 460-465. Print.
Weiner, Brian J and Maurice A Lewis. “The meaning of justice in safety incident reporting.” Social Science and Medicine (2011): 403-413. Print.
WHO. Improving health quality provision. Geneva: Alliance for patient safety, 2008. Print.
More than Words: conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety. Geneva: Alliance for patient safety, 2009. Print.
WHO patient safety Curriculum Guide for Medical Schools. Geneva: World Alliance for Patient safety, 2009. Print.
Wiegmann, Aaron Danish, et al. “Change Management in Health care organizations.” Leadership and Medical Service (2008): 701-712. Print.