Introduction
Approximately 25 million Americans are asthmatic, which equates to one asthmatic person in a group of 13 people. This data justifies the need to address the surge in the number of infected by assessing the quality-of-care asthmatic patients receive (Menzies-Gow et al., 2018). Furthermore, everyone is prone to contracting this disease, with social determinants of health such as contaminated water and food exposing people to the infection. On average, America reports ten asthma-related deaths daily, and therefore, developing a health improvement initiative that may enhance quality care delivery among patients is necessary (Menzies-Gow et al., 2018). This paper provides a framework for assessing the quality of care delivered to asthma patients and its impact on health improvement.
Data Collection
This study will incorporate asthmatic human participants among the most affected ethnic groups with different cultures, religions, sexual identities, and age groups. The study will commence after comparing the current health performance quality for asthmatic patients against the national average benchmark. The purpose of the study will be to provide an analysis of the quality of care delivery through an assessment of the participant’s health outcome. In addition, participants will be required to provide details of the state of their social determinants of health such as employment, education, access to safe foods, income, and safe housing (Oachs & Watters, 2016). This information is vital in providing insights into how the social determinants of health affect quality care delivery or enhance care provision among asthmatic patients.
Results from this study will initiate change in the underperforming areas of healthcare delivery to ensure that the standards of health provision are maintained. The study will take place for a maximum of 90 days to ensure that the data collected are accurate and reliable (Menzies-Gow et al., 2018). Within this time, significant changes will be observed, which are vital in making conclusions. The final verdict will depend on the assessment results, which will initiate a change strategy.
Data Collection Plan
Data collection in health research enables health systems to generate insights on the performance structure to develop improved systems. Therefore, technology will be a vital tool for this study because of enhanced accuracy, prediction, and data analysis. During the study, some of the systems to be used include the master patient index (MPI) system, remote patient monitoring system, and clinical decision support systems (CDSS) (Menzies-Gow et al., 2018). The Master Patient Index (MPI), also known as a patient master index, client registry, or customer registry, is a digital database that contains demographic data on every patient who receives medical services.
This system is accurate in prediction and can retain data for more than a decade (Menzies-Gow et al., 2018). Also, the study will utilize remote patient monitoring, which aids in sending communication between the patient and the expert on the health developments as they manifest. This system enables patients to monitor their symptoms and report any slight changes throughout the day. Additionally, the study will apply the CDSS system, which analyzes data and provides results based on patients’ health improvement or deterioration.
The Health Record Information Life Cycle
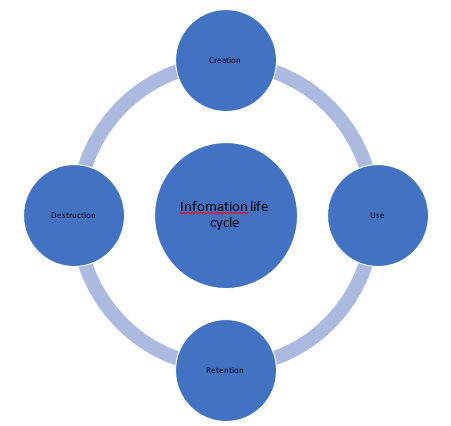
Figure 1 above depicts the life cycle of data whereby the process begins at creation and ends with the destruction of the information. The creation stage is when data is first retrieved either by verbal declaration or written communication from the participants (Menzies-Gow et al., 2018). This data can be typed as a document, recorded, or captured like a picture. The creation stage is where the team will gather the basic information for analysis. The utilization stage is when the retrieved data is used for the intended purpose. In this context, data retrieved by the team at the creation stage will be assessed to determine the quality of care given to asthma patients. The retention stage is when data is stored for legal, fiscal, or administrative purposes (Oachs & Watters, 2016). This research will utilize the retention phase to maintain an archive for reference in the study. Lastly, the destruction stage is where data is disposed to maintain the autonomy and security of the informants.
The Impact of HIE on Patient Care
Health information exchange (HIE) enables health practitioners to electronically share data securely to enhance quality, safety, and speed of care delivery. HIE improves patients’ care by reducing errors because many processes are digitalized. Also, the system makes care efficient by reducing unnecessary tests because the patients’ medical history can be easily retrieved, improving care. Also, HIE enhances clinical knowledge by enhancing collaboration among medical experts and patients, easing the exchange of information, which is integral in developing an effective diagnostic criterion (Oachs & Watters, 2016). Additionally, HIE enhances population health data by enabling health experts to analyze data from a broad spectrum which helps devise strategies to improve public health.
The health information manager is responsible for managing data retrieved by HIE. They are responsible for organizing, overseeing, and protecting patients’ data, including their medical history, diagnoses, and procedures. Health information managers should have a degree in health information management, understand the data protection laws and adhere to the guidelines (Oachs & Watters, 2016). In addition, they should be competent in technological operations such as the HIE systems to manage their work.
Data Security Plan
Data breaches, loss of data, and data theft are examples of threats presented by digital data sharing. One mechanism that could help maintain protected health information (PHI) is incorporating the access control feature to restrict unauthorized access to patients’ information. Access control is an integral security feature that applies the rule of authentication and authorization to limit unauthorized access to data (Oachs & Watters, 2016). This feature aligns with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requirements that mandate practitioners not to share PHI without the patient’s consent. Other rules to be applied include the HITECH Act which encourages the use of digital data management, such as coding PHI to ensure that data is safe from breach or misuse.
In addition, HIPAA applies the security rule, which will positively impact the health experts, policies, and procedures involved in this study (Oachs & Watters, 2016). For instance, HIPPA warns against sharing confidential information amongst health professionals if it does not impact the patient’s health. Also, HIPAA provides a framework for data sharing whereby all procedures are safe and operates within the ethical standards of practice, such as consensual data sharing.
Benchmarking Plan
Sources for national data will include patients’ reported data, medical records, and registries. These sources are vital for information because they provide accurate data. The sources for quality measures will include the national health standard metrics, health outcomes, available healthcare resources, care coordination, and patient outcomes. The national data provide the acceptable standard performance expected for hospitals (Oachs & Watters, 2016). This system will be incorporated into this study as a comparison metric to access hospital performance.
For instance, the standard permissible readmission rate stands at 22.0%, meaning that any hospital recording readmission of 22.1% and above is underperforming in quality care provision (Menzies-Gow et al., 2018). The team shall conduct a source audit to maintain data standardization to determine its efficacy in providing accurate data. Also, the team shall employ a data analyst to ensure that the retrieved information is correct. Data collected will be compared with the benchmark quality standards by averaging the scores related to the survey against the computed benchmark scores.
Quality and Change Management Strategies
Data findings from the study will be used as a metric to initiate change. For instance, high rates of readmission taint the quality of care delivery, meaning that the results will be used to develop initiatives that curb the contributing factors of readmission, such as medical errors or hospital falls (Oachs & Watters, 2016). Departmental workflow is enhanced by maintaining an inclusive stakeholder engagement, maintaining effective communication, and improving transparency. These variables are integral in change management because they ensure active team engagement. Research indicates that healthcare quality can be enhanced by incorporating technology (Oachs & Watters, 2016). This practice, alongside a better work environment for employees, is key to making changes. This study will be undertaken within 90 days in five steps, including developing the question, identifying relevant evidence, examining evidence, summarizing evidence, and interpreting findings (Oachs & Watters, 2016).
Conclusion
This study intends to provide a healthcare improvement initiative using data findings on the quality of healthcare service provided for asthmatic patients in the US. The study will take 90 days, whereby the human participants will be assessed to determine their satisfaction with service delivery and healthcare outcomes in different hospitals. In addition, this study will identify areas of underperformance to propose alternative strategies that could enhance healthcare delivery. The recommendations will enhance patients’ experience, improve health outcomes and prevent unnecessary loss of revenue in hospitals.
References
Menzies-Gow, A., Canonica, G. W., Winders, T. A., de Sousa, J. C., Upham, J. W., & Fink-Wagner, A. H. (2018). A charter to improve patient care in severe asthma. Advances in Therapy, 35(10), 1485-1496. Web.
Oachs, P. K., & Watters, A. L. (2016). Health information management: Concepts, principles, and practice (5th ed.). AHIMA Press.