Introduction
Practice development refers to a facilitated procedure in healthcare that aims to develop evidence-based and person-centered healthcare. It pursues to include individuals from every organization level to develop a positive impact on healthcare services. The procedure involves inclusive, collaborative, and participatory methods. However, the process does not involve several areas in the implementation of the practice. Practice development has obtained widespread use. However, it has limited application by other allied health practitioners.
Since healthcare services are offered in continuous change, modernization, transformation, and change applying strategical changes within the healthcare services to offer quality services has been complicated and disorganized. Practice development has transformed into an optimization tool to improve the quality of patient care. The approach has implemented evidence-based healthcare procedures that involve the use of the emancipatory method to provide person-centered healthcare (Roy, 2018). Practice development can be used to describe the mechanism for evaluating the daily practices ensuring that care providers are able to examine the daily services and adjust appropriately to improve the clinical results and boost the quality of the healthcare services.
One main objective of practice development is to alter the focus of the services to the client. In turn, work-based learning and person-centered traditions are the main factors in enhancing practice development. Individual-centeredness involves a plan to practice achieved by developing healthy relationships between the service users and care providers. Therefore, practice development has been used in several instances, such as developing shared principles, and service priorities, improving communication, and developing the safety and quality of healthcare as measures to improve the clinicians’ nature of services.
Role of Theory in the Design of Nursing Practice Developments
Effective nursing services demand the application of skills, art of care, and knowledge to provide quality, considerate, and effective healthcare to the patients who visit the health facilities. A significant form of knowledge is applied in the nursing practice development where research findings influence nursing decisions. Logically, the nursing practices should be based on study outcomes (Roy, 2018). Protocols followed in the nursing practices are derived from the nursing-based research findings. Similar to other industrial, commercial, and medical practices, the quality results are influenced by implementing the research findings. Theoretical designs in the development of nursing practice help in defining or testing novel practices in nursing. Theories in nursing development help in guiding the process of research procedures and developing new testing methodologies.
The critical function of nursing theories is to help improve the general practices that positively impact the quality of health services and improvement of the patient’s life. Nursing practice is based on the development of nursing theories. On the other hand, nursing theories are verified by the practice, and hence the relationship between the nursing theory and practice is reciprocal. Many calls include theory in professional practice, but this has been fragmented and remains unrecognized by several nurses. There is a need to include the reciprocal relationship between the nursing theories, research, and practice, the increase in the capability of nursing practices in fulfilling the community demands. This will be essential to fulfill the gaps that have been observed in nursing practice development. In this research, humanistic nursing theory and its implications will be analyzed.
The Strengths and Limitations of the Application of Theories in Nursing Practice
Strengths
The nursing theories provide an integrated foundation of nursing practice. The theories are functional in the education, administration, research, or clinical setting. They help the nurses who are beginning their professional carrier to learn from those who have already been in the field and have gained enough experience. The other strength of the nursing theories is that they support a strict adherence to the nursing procedure while attending to the patients, offering quality healthcare services to patients. Nursing theories are complementary since the theories are developed from research outcomes. Many theories have shown in many areas where a nurse can cross-reference and supplement the information obtained from one theory. The importance of nursing theory can be observed in the empiricism of the theories. It offers practical or functional factors of the theories and has enabled the development of the academic component of nursing. The strength emphasizes the nursing ethics and provision of quality and dignified patient care. Having knowledge about patient conditions, nurses can provide enhanced patient care within the facility.
Limitations
Nursing theories involve descriptions that should be applied in practice. They are a systematic way to broaden the application of nursing practice. However, there are limitations associated with the theory. Nursing theories are often general, and, therefore, it can be a mistake for clinicians to apply general nursing theories in treating specific patients’ needs. Middle-range theories serve as a framework for research in nursing practice whereas the middle-term nursing theories are shorter than general theories, the greatest challenge is observed in implementing the recommendations of the theories. While the middle-range theories provide detailed guidelines for nurses, such theories are not applicable for specific and unique healthcare challenges.
In Orem’s theory, there is an unclear description of nurse-society connection, public education, and family, critical in the treatment and management of patient issues (Bliss et al., 2017). Though the community, family, and the environment are involved in self-care, the main focus is on individuals. Another weakness found in the nursing theory is the definition of health, which is considered as a constantly changing and dynamic state that ranges from illness to wellness, non-health, or health. Its definition in this theory contradicts personal patient experiences with different health needs and care levels.
The other limitation associated with nursing theories is that nurses often expect too much from the theories. Nursing practice development theories provide reliable solutions to deal with specific challenges in a defined population; the limitation is that the theories have a slight relation to fundamental nursing research. Weaknesses in the nursing theories have been observed in the formulation process, which mainly focuses on physical healthcare and neglects patient health’s emotional and psychological aspects. This is evident in Orem’s theory, which mainly focuses on physical health and neglects emotional health in the nursing theory description (Alligood, 2017). Nursing theories represent the subjective view of the nurses that construct them. The key to this is that the conceptions of the theory developers are biased because of the individual experience of those who develop the theories
Areas of Adjustments in the Nursing Practice
Dramatic changes in the last decades have characterized healthcare services. It, therefore, required that the nursing operations should also adjust appropriately to meet the care demands. With the development of the new trends, nursing operations should include cost-effective approaches to providing quality care. Nursing organizations have reported various strategies that should be adopted to meet the demands. The recommendations include adopting novel models in care delivery without interfering with quality. Such strategies include making changes in labor patterns, which may result in improved quality and safety of patient care, limiting and laying of unnecessary cost repression scales that will ensure the replacement of less qualified practitioners with more qualified nurses.
Since the lack of redeployment approaches and education has greatly affected the nursing sector, it is recommended to enhance sufficient supply to prepare the registered nurses for future demands. In addition to the developing trends, research on healthcare services has shown that there is a limited number of nurses in hospitals and clinics, which has compromised patient care quality. The number of nurses should be increased which will ensure a decline in the mortality rate as well as reduce the congestion in the earth facilities.
Cultural awareness is primary in the delivery of better healthcare services. Diversities in cultural beliefs influence patients’ views of healthcare services. Understanding, accommodating and respecting the patients’ preferences according to their beliefs, and traditional and cultural practices should be included in the development of nursing care services. Recognizing individual biasness is the initial step in understanding the cultural diversities of patients. Nurses should show high levels of professionalism because the outside look portrays an individual’s moral values and ethical principles. Handling the work with much professionalism indicates dedication to the duty, which influences the confidence of patients. The nurses should show high levels of discipline and respect to both their colleagues and patients.
The level of attention that practitioners give to the patients should be increased. Sticking to one normal routine in healthcare providers may be cumbersome and monotonous to the healthcare providers. Therefore, it is recommended that developing alternative healthcare procedures may be enjoyable and increase the quality of care provided. In this case, the practitioners should think of people-based care practices rather than common task-based practices. Creative and critical thinking should also be adopted in nursing practices. This will allow the practitioners to be problem solvers and reduces the dependence on nursing theories, doctors, and health organizations in solving daily challenges. The nurses are required to identify the problems and discuss the possible solutions with their fellow nurses. Since nurses are the mediators between patients and other service providers, the nurses are required to effectively communicate with the patients as well as the other care providers.
Humanistic Nursing Theory
Humanistic nursing focuses on the human factors in nursing practices. It was developed by two doctors: Loretta Zderad and Josephine Paterson. The theory is based on incorporating existential and phenomenological theories. The doctors were convinced that by evaluating their personal experiences with the patients, nurses would develop argumentative theories that can help in their daily practices. The theory states that in order to increase the patient experience, a nurse should have a personal connection with the patient, which will enable them to offer quality services. The theory can be presented in the figure below. (See Fig. 1)
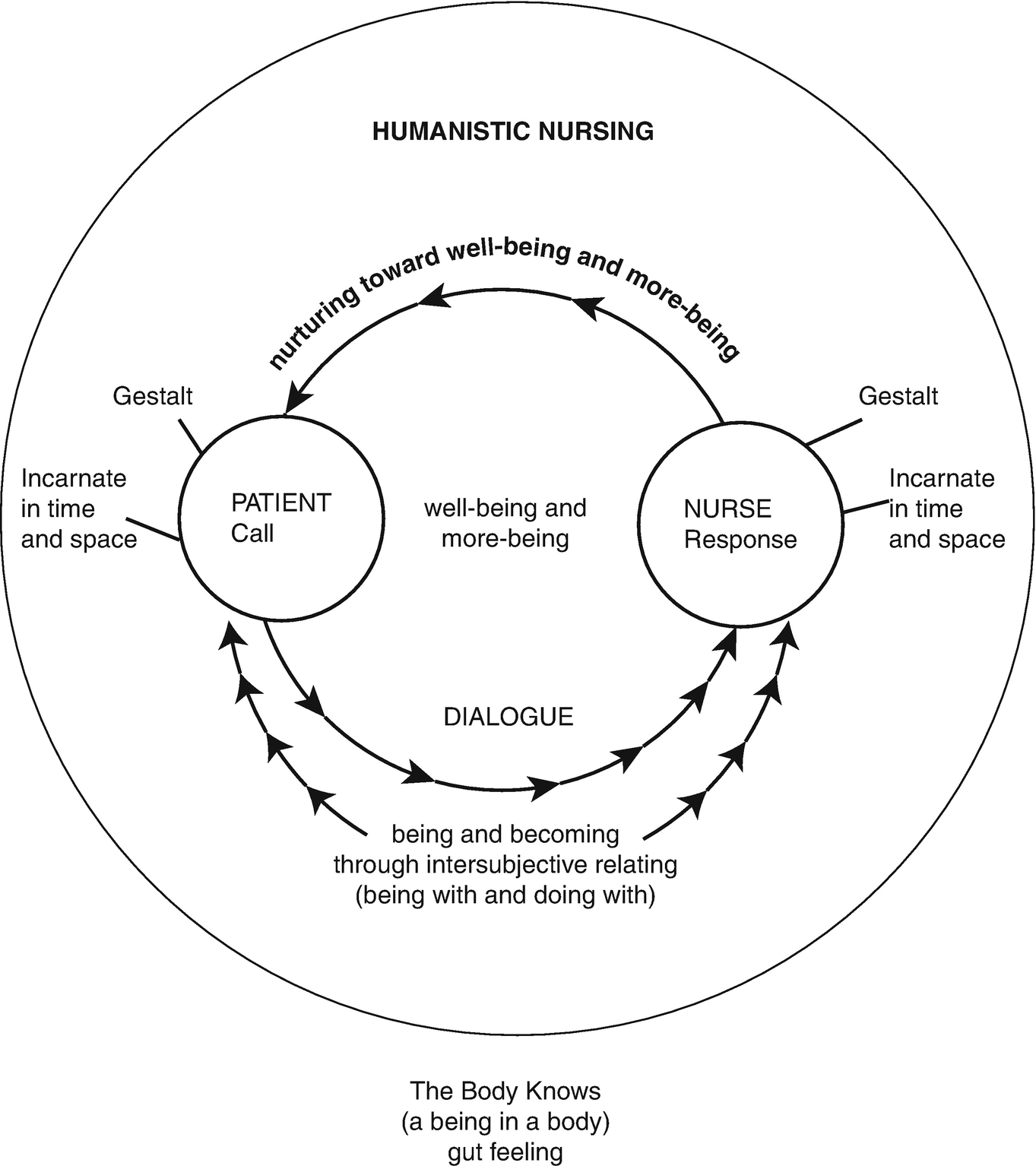
The theory requires the nurses to have conversations with the patients that will enable them to join the patients’ emotional and psychological needs that will help find the patient’s viewpoints and perspectives and hence influence the quality of healthcare. Through the application of the concepts, in theory, nurse educators can help the trainees understand that how they relate with their colleagues and patients is important in providing quality health. The aspects of the theory include
Dialogue that involves developing communicative connections is subdivided into person-to-person dialogues, person-to-object dialogues, and group dialogues that involve communities or specific target groups: The community where more than two people are cable of discovering their conduct’s innate meaning through sharing of experiences. Phenomenological Nursing intends to assist nurses in defining their experiences in the context of dialogues. Phenomenological nursing consists of five distinct phases. This includes getting ready to understand perceptions and experiences without judgment or prejudice and at the same time considering personal views. Preparing to listen to other people’s experiences whether nurse or patient, recalling past experiences to classify, compare and analyze personal experience with other person’s experiences, evaluating the information found in the first three steps, and applying the ideas that have been recommended from every situation in making conclusions through enhanced understanding.
Use of Metaparadigm
Metaparadigms define the overall factors in scientific discipline and efforts. Metaparadigms involve a number of factors and particular paradigms. Fawceti first characterized nursing meta paradigms into a person, health nursing, and the environment (Watson, 1999). The human aspect refers to people in a distinctive family, society, and culture. Health meta paradigms include life and death processes. The environmental meta paradigms are categorized into global, regional, and national social, cultural, economic, and political factors. The personal meta paradigm involves nursing practices, the nursing profession, nursing goals, and outcomes. Complimentary to the initial meta paradigm, various other meta paradigms have been developed. For example, Watson included nursing care as a key representation of nursing practice that makes nursing care the other meta paradigm. In recent decades, the nursing curriculum has been developed from conceptual frameworks. Theoretical frameworks are also considered in the development of nursing concepts and values. It is significant for professional nursing students to integrate clinical experiences into conceptual understanding. The nursing meta paradigms allow the nursing students to tolerate the challenges they are likely to face when establishing their career identity.
Strengths of the Theory
The development of theories motivates the nurse, which ultimately reflects on their performance. It motivates the nurses to develop goal-oriented characters that will improve healthcare quality in the facilities. The theories help boost the nurses’ abilities to continue working; however hard the task may be with the significant objective of accomplishing the appointed task. The development of theories while considering environmental factors is essential in ensuring optimal performance. Failing to apply the concepts in the development of the theories will lead to a confined view of nursing practices that will reflect the practitioners’ quality of healthcare.
Evaluation of Humanistic Theory
In evaluating the humanistic theory, researchers should include the three concepts of the theory in conjunction with meta paradigms. The evaluation will find out the number of dialogues that various nurses have had with their patients and get to understand the experiences of both the patient and the nurses. The experiences will act to determine the applicability of the theory since researchers will be able to evaluate the responses from a number of patients and nurses. The evaluation can also be achieved by surveying the implementation procedures of the theory.
References
Alligood, M. R. (2017). Nursing theorists and their work (1st ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences.
Bliss, S., Baltzly, D., Bull, R., Dalton, L., & Jones, J. (2017). A role for virtue in unifying the ‘knowledge’and ‘caring’discourses in nursing theory. Nursing Inquiry, 24(4), e12191.
Kaakinen, J. R., Coehlo, D. P., Steele, R., & Robinson, M. (2018). Family health care nursing: Theory, practice, and research (1st ed.). FA Davis.
Kitson, A. L. (2018). The fundamentals of care framework as a point-of-care nursing theory. Nursing Research, 67(2), 99-107.
Roy, C. (2018). Key issues in nursing theory: Developments, challenges, and future directions. Nursing research, 67(2), 81-92.