Physical examination
The components of the physical examination include the following:
- Palpation: this refers to a situation where the examiner locates something in the body by feeling it with bare hands.
- Percussion: Involves the act of gently tapping the body to assess any sign of ailments.
- Inspection: this is the use of eyes to observe the body and note the ailments. (Bickley and Bates, 2007)
- Auscultation: use of a stethoscope to hear sounds of movements in the internal organs.
Measurement of blood pressure
The sphygmomanometer is the most common method of measuring blood pressure. A stethoscope, attached to a sphygmomanometer and a mercury manometer together with an inflatable cuff is wrapped around the arm of the patient, the cuff is then ballooned with air through a rubber bulb to obdurate the artery, the stethoscope is then used to listen to the arteries as pressure is released from the cuff.
Recording of the blood pressure value follows a specific format, the numerator is the systolic pressure meaning the pressure in the arteries when the heart muscles contract. It has a higher value than the denominator. The denominator is diastolic pressure, referring to the pressure in the arteries in between heartbeats or when the ventricles are filled with blood. The normal blood pressure is120/80, although it varies.
Pulse rate
The numeric difference between the diastolic and the systolic pressure is called the pulse pressure, this value is applicable in the evaluation of the intensity or force that the heart uses to pump blood. It is used to monitor the pumping activity of the heart. (Bickley and Bates, 2007)
Blood pressure cannot remain constant, it keeps on changing. However, there are ranges set to establish the normal pressure. The accepted values of systolic pressure lie between the range of 100 and 140. Values below or above 100 and 140 reflect low and high pressure respectively; Mr. Smith’s value indicates high systolic pressure.
The normal diastolic pressure is between the range of 60 and 90, Mr. Smith’s value is relatively higher, indicating mild high blood pressure. He is likely to experience health issues like chest pains, dizziness, nausea, and blurred vision. From the results observed, the following lab tests were performed: Blood glucose level, serum test, blood tests, platelet count, urine test, arterial blood gases, and immunoassay. Consequently, serum, urine, and blood samples were used.
Platelet count
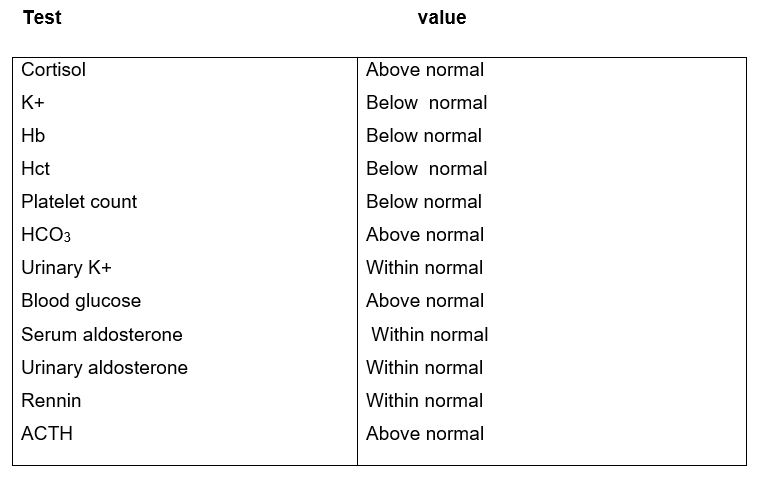
The normal platelet range for a healthy person falls within a range of 150 and 400×109 for every Litre of blood. Smith’s history of cancer made platelet count necessary, lower levels reveal cancer chemotherapy, leukemia or deficiency of vitamin K.Higher values indicate anemia.The table below indicates the values of the tests as compared to the normal range.(Cheriyan and Wilkinson, 2010)
Imaging
CT scan is used to generate 3 dimensional images of internal organs, In diagnosing cancer of Mr. Smith, the CT scan and MRI imaging system were used. The CT scan uses X rays while the MRI uses radio waves in imaging, however, both use waves in imaging. CRT and MRI confirmed cancer in Mr. Smith
References
Bickley, L. S., Szilagyi, P. G., & Bates, B. (2007). Bates’ guide to physical examination and history taking (9th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.print
Cheriyan, J., McEniery, C., & Wilkinson, I. (2010). Hypertension. Oxford: Oxford University Press.Print