Abstract
Every worker in each field is susceptible to injury in their workplace. However, health workers face a higher risk of injuries in developing many disorders such as back pain, muscle pain, and soft tissue-related pain known as musculoskeletal disorders. This population is experiencing higher rates of occupational accidents compared to other industries, consequently becoming a serious public health concern. The need for immediate attention to this problem can be justified by health impacts and other related outcomes related to these events, including absences. The rates of injuries suffered at work among nurses and nursing assistants in the United States were 13.6 cases and 19.2 per worker, respectively (McCaughey et al., 2016, p. 2). The purpose of this project proposal is to find innovative ways of reducing secondary occupational injuries among healthcare personnel. An integrated solution is presented in this report to provide healthcare facilities and institutions with a foundational framework for the prevention of secondary workplace accidents. The proposed solution consists of several interventions, including staff employee training and education, financial incentives, and legislation and enforcement, promoting a strong safety culture, embedding ergonomics interventions, strengthening exercises, fitness training, and compliance inspections.
Introduction
Unintentional injuries among workers in different sectors and industries are a major public health concern. Workplace injuries cause serious health impacts on the already vulnerable populations and other related outcomes related to these events, including absences (Apostolico & Shendell, 2016). Musculoskeletal injuries are the primary cause of accidents that necessitate absence, accounting for 34 percent of cases of absenteeism reported by nurses and nursing assistants (McCaughey et al., 2016, p. 2). A workplace injury is unavoidable, but the impact and the reoccurrences can be prevented to protect the workers from long-term disabilities (Zahra, Elmoaty Sheha, & Elsayed, 2020). This disorder affects the muscles, nerves, and tendons, and the most common symptom is back pain.
Working as a care provider involves many movements, especially during emergencies, and manual handling of patients, which is considered the critical contributor to this public health problem. Moving patients requires several postures such as bending and stooping, physical strength and manual force, and a lot of movement (McCaughey et al., 2016). These activities can cause damage to the muscles and the skeleton. Such events increase with the length of practice. In addition to that, health workers are exposed to several infectious diseases because of the nature of their work. Handling clients without personal protective equipment (PPE), such as masks and gloves, exposes healthcare providers to infections. This report proposed an innovative solution for reducing and preventing secondary injuries in the healthcare sector. An extensive review of the empirical literature is undertaken to find the most effective way of addressing and improving workplace safety concern.
Goals and Objectives
This project proposal aims to find innovative ways to minimize the incidence of secondary occupational injuries and reduce the related health impacts. The specific objectives of the project are:
- To identify workplace injuries that health workers sustain and find prevention measures.
- To find a solution to prevent the recurrence of workplace injuries
- Develop effective tools and strategies to help injured workers avoid subsequent injury
- Develop effective programs and supports to assist healthcare workers who sustained injuries while on practice to return to full health.
Background
There is a growing concern over workplace injuries in the healthcare and social assistance sectors. The occupational injury rates of nurses and nursing assistants working in public healthcare facilities were estimated at 13.6 cases and 19.2 per workers, respectively (McCaughey et al., 2016, p. 2). Consistently, a recent study of insurance claims related to subsequent occupational injuries among New Zealand workers established that 58% and 31% of the participants reported at least one and multiple injuries in 24 months, respectively (Harcombe, Davie, Wyeth, Samaranayaka, & Derrett, 2018). These statistics prove that healthcare practitioners are at a greater risk of sustaining an injury at work. Therefore, there is a strong need to develop innovative strategies and solutions to help curb this problem.
Theoretical Foundation
The proposed solution combines employee training and education, financial incentives, and legislation and enforcement of workplace safety standards. Other interventions include promoting a strong safety culture, embedding ergonomics within organizational processes, strengthening exercises, fitness training, and compliance inspections on injuries in the workplace. This integrated approach is justified by the fact that occupational injuries are complex and multifaceted (Pietilä, Räsänen, Reiman, Ratilainen, & Helander, 2018). Figure 1 below demonstrates that accidents at work are attributed to many factors.
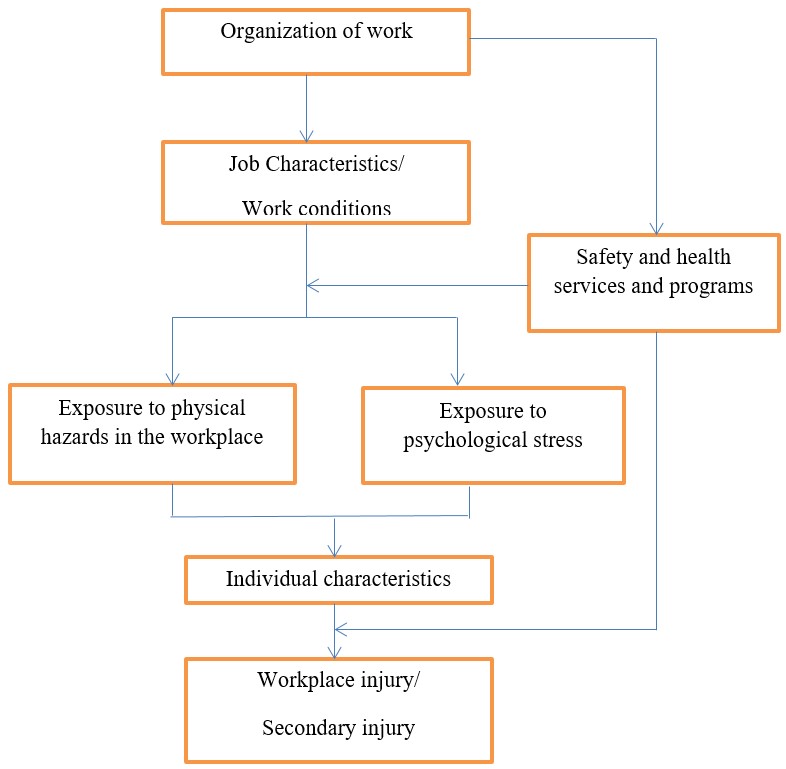
Education and training can help healthcare workers recognize and avert potential injuries at work. A practical session should be carried out once in a while for the workers and even medical students. It will provide them with the basic knowledge on how to recognize, handle, and avert hazards that might cause injuries at work (Teufer et al., 2019). They should also be educated on how to take care of themselves when managing patients with chronic and infectious diseases. They should learn to cover themselves and avoid contact with patients to avoid getting infected. Training and education enhance prevention of occupational injuries and hazards (Teufer et al., 2019). Therefore, this intervention will promote safe work practices, risk reduction, proper utilization of protective equipment, and compliance with safety measures.
Furthermore, providing health workers with PPEs is an evidence-based strategy to avoid future injuries. These tools will help reduce the force and movement of the workers reducing muscle work. Health facilities should provide masks, gloves, face goggles, isolation gowns, and sanitizers to the workers when handling patients to reduce infections. Health and safety policies and a strong workplace safety and safety culture will be considered to enhance organization wide safety compliance. These guidelines will heighten injury prevention efforts and ensure employers take responsibility for the workers (Apostolico & Shendell, 2016). The initiatives will help address physical and psychological risks at work.
Moreover, ergonomic Interventions, such as increasing the number of health workers, can help mitigate the risk of ergonomic hazards. Instead of putting pressure on one health worker, the workload can be divided among many workers. It reduces the burden placed on an individual worker. Regarding lifting, having several workers can help out, so they are not lifting much load. People get injured more often because they lack a helping hand due to a shortage of workers. It will be of great help to the employment sector as more workers will get employed. Observing physical fitness can help avoid muscular and skeletal disorders. Other strategies that have demonstrated positive outcomes include sstrengthening exercises, fitness training, financial incentives like insurance premium discounts, and compliance inspections on injuries in the workplace.
Data and Discussion
This proposal will enhance health workers’ safety within their areas of service. The project will meet all the requirements needed to protect the workers from secondary injuries (Pietilä et al., 2018; Harcombe et al., 2018). For instance provision of tools to health workers such as PPEs will protect the health worker from contacting communicable infections. The provision of sliding sheets for carrying sick patients will reduce the strain on the health workers. It will lower their chance of getting the muscular skeleton disorder.
In another instance, development and support such as health and safety policies guarantee the workers’ safety. In case of an injury, this policy will ensure that the employer takes accountability. The programs can include counseling and psychological help. It may be useful when a traumatized personnel needs help and support to return to total health. Educating them once in a while on how to protect themselves while at work will promote long-term prevention. Maybe these injuries are experienced because they don’t have complete knowledge of how to handle themselves. Practical sessions, especially on taking patience and training on protecting themselves, should be carried out. Therefore, effectively implementation of this proposal will benefit health workers and the society.
Conclusion: Implementation
The proposed project targets workers in the in healthcare and social assistance sectors. They include nurses, doctors, physicians, pharmacists, radiologists, lab technicians, and social workers. Healthcare facilities will be required to take ensure implementation of the suggested occupational health and safety promotion interventions and compliance with other relevant OSH standards. Part of the project solution is the requirement for personnel to work safely and adhere to workplace safety standards. It takes less than a year to implement this proposal since every solution will be carried out efficiently by the health ministry.
It can be implanted by funding hospitals and health facilities financially. The funding will help in purchasing more equipment such as the sliding sheets and the personal protective equipment. The ministry can also implement the proposal by employing more workers to reduce an individual worker’s workload. I believe this proposal is worth investing in, and its implementation will create a better working environment for the workers. It, in turn, will benefit society.
References
Apostolico, A. A., & Shendell, D. G. (2016). Injury surveillance and associations with socioeconomic status indicators among youth/young workers in New Jersey secondary schools. Environmental Health, 15(1), 1-9.
Harcombe, H., Davie, G., Wyeth, E., Samaranayaka, A., & Derrett, S. (2018). Injury upon injury: A prospective cohort study examining subsequent injury claims in the 24 months following a substantial injury. Injury Prevention, 24(6), 437-444.
McCaughey, D., Kimmel, A., Savage, G., Lukas, T., Walsh, E., & Halbesleben, J. (2016). Antecedents to workplace injury in the health care industry: A synthesis of the literature. Health Care Management Review, 41(1), 42-55.
Pietilä, J., Räsänen, T., Reiman, A., Ratilainen, H., & Helander, E. (2018). Characteristics and determinants of recurrent occupational accidents. Safety Science, 108, 269-277.
Teufer, B., Ebenberger, A., Affengruber, L., Kien, C., Klerings, I., Szelag, M.,… Griebler, U. (2019). Evidence-based occupational health and safety interventions: A comprehensive overview of reviews. BMJ Open, 9(12), e032528.
Zahra, N. A., Elmoaty Sheha, E. A. A., & Elsayed, H. A. (2020). Low back pain, disability and quality of life among health care workers. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Allied Sciences, 9(2), 34-44.